The theory of evolution - myth or reality?
- Introduction
The theory of evolution is taught today in schools as a proven and undisputed truth about the origin of species, including man.
Although its promotion has an absolute character, similar to a religious dogma, the theory has many loopholes, even recognized by its promoters. At the same time, there is an accreditation of the idea that those who reject the theory of evolution can only be religious fanatics who refuse to know the "scientific evidence". In reality, you do not have to be religious to doubt this theory. At the same time, many religious people reject evolutionism precisely because they have researched the so-called evidence proposed by it.
In this paper we will present these problems and show that adherence to this theory is rather an act of will and faith, rather than a logical conclusion deduced from reality on the ground.
- Charles Darwin and his theory
Following biological observation trips in the 1830s, during which he encounters numerous varieties of insects, plants and animals in different places of the world, British naturalist Charles Darwin formulates the theory that lower life forms have evolved, through countless intermediate forms, to higher life forms. This transformation began five to six million years ago, when the earth was inhabited by a multitude of intermediate forms that were born, lived and obviously died. Darwin published this theory in 1859 under the title "Origin of Species."
- What does theory of evolution say?
The theory of evolution exists in two main variants.
In the first version (launched by Darwin), it is stated that the lower life organisms and forms of life have evolved linearly (slowly) to superior forms. More specifically, whole populations of each species have "gradually" moved, through many intermediate forms over millions of years, to superior forms.
If we are to represent the evolution of a species to another species, for understanding the theory we will represent the original species with a color and the final species of another color - see the figure below. The initial black species slowly transforms and passes through a variety of intermediate-form shades until it becomes a white new species. It would have evolved all the species, each with hundreds of thousands of copies that have gone through this evolution.
Two were the main determinants of these transformations:
Natural selection. Following a random process, inferior forms of life have adapted and transformed into changing environments, thus emerging new forms of life, of which only survivors survived - the higher ones.
Genetic mutations. For evolutionists, the similarities between the genetic codes of some species are evidence of transformation of one another. As a result of the influence of viruses or radiation (cosmic, etc ...) on lower forms, genetic mutations have occurred at DNA level that have transformed some species into other species.
The second version of the theory, which appeared more recently because of the problems raised by the former, states that evolution took place not in a linear fashion, but in leaps.
We will explain below the problems of both versions of the theory.
- Lack of intermediate forms
The main problem of the theory of evolution is the lack of intermediate forms, both dead and alive.
If at every moment during the gradual evolution there were many living intermediate forms that have lived on earth for at least several generations, after which they have died, their fossils should be found today in the earth, not only for a species, but for all species, since we affirm that all species have evolved - see figure above. However, what we find today in geological strata are the fossils of distinct species, far from one another, which is no longer present today, but about which evolutionists try to say that they have evolved from one another.
Darwin was first aware of the problem of fossil failure, but he confessed to the belief that they would eventually be found. This discovery is still to be expected. For example, if in the geological layer A we find fossils of the X species and in the C layer we find fossils of the Z species, which are (indirectly) drawn from the X species, it should be found in layer B, which corresponds to the intermediate period, a hypothetical intermediate Y species. However, we can not find these intermediate fossils, but also the X and Z fossils and other unrelated fossils of type V, W, etc. Moreover, archaeologists have discovered that during the Cambrian period, a lot of species suddenly appear, as nothing, in a phenomenon called today "the Cambrian explosion."
Slow evolution from one species to another involves a lot of intermediate forms. Hundreds of thousands of copies from each intermediate level are not found at fossils.
- Human evolution and the problems of the theory
According to the theory of evolution, there are four great categories of ancestors of man:
Australopithecus (any form that belongs to the genus Australopithecus)
Homo habilis
Homo erectus
Homo sapiens
The first category includes the most prominent ancestors of man - Australopithecus means "southern monkey". They are believed to have appeared in Africa 4 million years ago and disappeared a million years ago. The oldest subdivision, says evolutionists, is Australopithecus afarensis ("Lucy"), followed by Australopithecus africanus and Australopithecus robustus, which had relatively larger bones.
Although they had monkey-specific and living-tree features, evolutionists claim that they were walking in two legs. However, other evolutionary scholars (Lord Solly Zuckerman and Charles Oxnard) have shown that the Australopithecans did not walk in two legs.
Lucy
By far the most important "proof" of man's theory of evolution is Lucy, a fossil found in Ethiopia in 1974. Fosila represents 40% of the skeleton of a bipedal primate. Evolutionists compared the size of Lucy's skull to the size of the skull of a monkey and a modern man and found that Lucy was in the middle, where they concluded that Lucy was an evolved primate - biped and skull evolved from monkey to man. Later, at the end of 2008, the researchers realized that Lucy was not a female, but the male and Lucifer baptized him!
The problem with Lucy and implicitly with the deductions of evolutionists is that Lucy's skull has found such a small fraction that the size calculated by evolutionists is very questionable. Moreover, the analysis of her fingers shows unequivocally that Lucy lived in trees, something also recognized by some evolutionists. Other evolutionists, however, think that Lucy was not an evolved monkey, but a variety of African primate that later disappeared as a species. This assumption is also reinforced by the fact that in the same region and only in that region other fossil traces of what evolutionists call Australopithecus afarensis (Lucy species) have been found.
Also, in the region and dated as of Lucy's time, human traces were found. If Lucy lived in the same period as humans, he could not be their ancestor.
Homo habilis
It has somehow emerged from the need to connect Australopithecus and humans, the first being too different from the last (Australopithecus were, in fact, monkeys). So evolutionists took other monkeys fossils and presented them as being different from Australopithecus. In addition, they said that these "ancestors" used tools (Homo habilis means "handsome man").
But even studies of evolutionists (Wood & Brace and Holly Smith) have emerged that have shown that Homo habilis were not different from Australopithecus, being in fact monkeys.
Homo erectus
The Homo erectus category includes several hominid discoveries. This includes the Pekin man, the Java man and the first Homo African specimens such as Turkana Boy. Homo erectus is described as a small person with an average cranial capacity of 973 cm3, which would place it at the bottom of the modern human beach, ranging from 700 to 2,200 cm3, according to Molnar, Races, Types, and Ethnic Groups (1975). Generally, Homo erectus bodies are illustrated as very similar to modern humans, but with thicker bones. The skull of Homo erectus was classified as more primitive. Thick prickles, flat and receded forehead, lower and outward mandible and large teeth are considered to be primitive features.
However, the Neanderthal man also presents these characteristics, but he is considered to be human. It can be said that Homo erectus is actually a smaller version of Neanderthalian.
Harry Shapiro writes in his book, Peking Man (George Allen & Unwin Ltd, London, p. 125):
"But when examining a classic Neanderthal skull, of which we now have a large number, we can not fail to conclude that its fundamental anatomical structure is a larger and more developed version of the skull of Homo erectus. Like Homo erectus, it has an occipital exit, thick eyebrows and a relatively flat crown. Its largest width is low and is immediately above the ears, and the absence of a beard outside is typical. "
He says these things at a time when the people of Neanderthal still had a gross reputation, but that does not change the implications. Homo erectus was considered to be a little closer to monkeys than we are, but if it was a smaller version of Neanderthal, its features should not be considered primitive. In fact, the Aborigines in Australia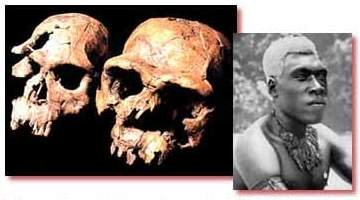
The prominent eyebrows and hooded forehead of Homo erectus meet in several of today's human varieties, such as the Malaysians.
The man of Neanderthal. Status and theory twists
Evolutionists can not decide where to place on the scale of evolution the one called them "the man of Neanderthal." It is presented as a subspecies of Homo sapiens, when it is a separate species (Homo neanderthalensis).
First it was said that it was a species different from Homo sapiens (modern man).
Subsequent research then showed that the Neanderthal man lived in the same period as Homo sapiens. The two would have had a common ancestor, but would have evolved differently. We ask, however, how can two copies live in the same age and geographic area differently?
Then it was discovered that the Neanderthal man was smarter than he is portrayed in the semi-human gross paintings. According to Live Science's edition of November 15, 2006, "anatomical excavations and studies have shown that Neanderthals used tools, wore jewelry, bury their dead, cared for the sick, and possibly sing or even talk like us. Though much more modest, their brain was slightly higher than ours. " The Neanderthals also were wearing clothes.
It was said that the man of Neanderthal not only lived at the same time as Homo sapiens, but also had intimate relationships with him! One in two: or the two were in fact the same species (they had the same genetic code and they were simply humans), or Homo sapiens made some big confusion in choosing their partners. This imprisonment would have led to the assimilation of the countryman by Homo sapiens.
In 2012, a new hypothesis was launched: the Neanderthal man disappeared long before Homo sapiens, then re-emerged (from where?) For a short time (?), Eventually disappearing definitively before the appearance of Homo sapiens .
The problem becomes even more complicated by the existence of several simultaneous hominids - denizovians (built on the basis of a finger fragment found in Siberia in 2008), Indonesian hobbits and the Chinese deer population. These "species" or ancestors of man make the theory of evolution itself to be in a continuous transformation and lead to the credible hypothesis that these species were no other than regional variations of the human species, as it is today. This hypothesis is reinforced by the fact that denizovians have genetically influenced the aboriginal populations of Australia and some Melanesian peoples, and Neanderthals have genetically influenced all branches outside Africa.
In fact, at the 1958 International Congress of Zoology, Dr. A. Cave stated that he had researched the fossils of the "Neanderthal Man," and his conclusion was that the Neanderthal had been nothing but an old man with arthritis.
On the other hand, in his book Buried Alive, orthodontist Jack Cuozzo describes the poor reconstruction of Neanderthal skulls in order to present them as more primitive and more similar to monkeys. For example, Cuozzo says the Le Moustier specimen has been rebuilt so that its mandible looks more simian than it would have been.
There is no doubt that the Neanderthal man was an ordinary man.
Today there are many types of people on the Earth's surface. Their skeleton is different (influenced by style and environment), the shape of the skull is different, but they are all people. It is possible that, over a thousand years ago, an actual skull of a particular form is classified as belonging to an ancestor of man, only because it is different from a standard arbitrarily chosen by evolutionists.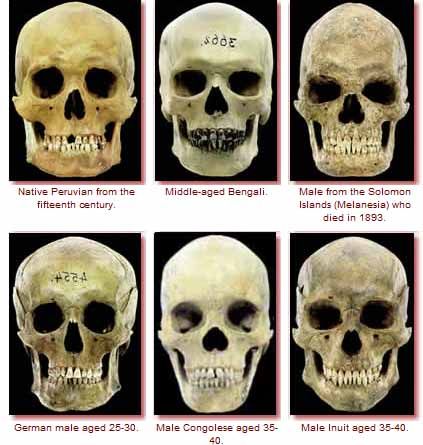
Peruvian sec. XV - Middle Aged Bengal - Adult from the Solomon Islands, sec. XIX
German Young - Congolese average age - Medium-age Inuit
Starting from very few and very interpretable fossils, the evolutionary artists were quick to paint pictures of our "ancestors" - creatures with humanoid figures but with a body similar to monkeys. Such representations, the fruit of imagination, can be seen in school textbooks and natural science museums. The images are made in detail (based on a few bones found) and have the power to pass as evidence. Lucy found about 40% of the skeleton, but natural science museums exhibit Lucy's complete copies from head to toe - see examples of evolutionary art here.
All the fruit of imagination is also the evolutionary tree that presents fantastic animals that would have evolved to the species existing today. Why would it raise fish legs? Was he bored with the aquatic environment and decided to visit the dry land? As long as fish have existed and continue to exist, the theory of fish reptile evolution is a fairy tale.
After finding a few fossils they presented as intermediate links, evolutionists realized that they can not prove with a handful of fossils the evolution of all species. So we find out, at least from the Encyclopedia Britannica, that today no fossils are sought, BUT that the theory of evolution is already demonstrated! How? Through studies and findings in the fields of genetics, biochemistry, biology ... For any religiously or anti-religiously unmotivated mind, the empirical conclusions drawn from these areas can not provide answers to the fundamental question "Where are the intermediate, dead and living forms?"
Given the lack of such elementary evidence to underpin the evolutionary scenario, we are more likely to believe that those fossils, few in number and far from other species, belonged either to existing species (Lucy was a monkey, the man of Neanderthal was man ...) or to missing species today.
The problem of lack of intermediate forms is not limited to fossils in geological layers. The question is: does the development continue today or has it stopped?
If it continues, where are the intermediate forms of life? Why do not I still live intermediate species between monkey and man? What we see in nature: Well-defined and long-distance species. It is rational to believe that this distance has always existed between them - there has been no evolution.
Returning to the idea of natural selection, although it is certain that changing environmental conditions can force the creatures to adapt, we must not confuse the adaptation with the evolving. Some animals can adapt within certain limits, but they remain within their species. If environmental conditions require an adaptation beyond their possibilities, those animals disappear, they do not evolve in anything else, as was the case with dinosaurs.
If an African moves to live at the North Pole, perhaps in time, the color of his skin will change to some extent, but he will still remain. It will adapt, but it will not evolve into anything else.
Counterfeit evidence
From the desire to produce at any cost a "missing link," some evolutionists even recourse to the fossilizing of fossils that they presented as evidence of evolution. There have been so famous cases of fossils of "human ancestors" that have subsequently proved to be either simple people, monkeys or ... pigs.
The man of Piltdown
The "Piltdown Man" (a jaw and a piece of skull) was discovered in 1912 in England. Although the jaw was closer to the monkey, the teeth and the skull were closer to the man. It has been said to be 500,000 years old and has been exhibited in many museums as an absolute proof of human evolution. For over 40 years, numerous articles have been written and over 500 doctoral theses written on behalf of the Piltdown man.
In 1949 he tried to re-dated with a new fluoride test. It was found that the jaw contained no fluorine - it was very recent. The skull contained a small amount - it was several thousand years old. It was found that the jaw had belonged to an orangutan, that the teeth were piled and that the tools discovered with the "ancestor" had been made with modern means.
The "Man of Piltdown" was retired from "evidence" in 1953.
The man of Nebraska
"The Nebraska Man" (a tooth) was discovered in 1922 in the US. It has been said to have features between the monkey and the man.
The belief in that tooth, that he was an ancestor of man, was amazing. Based on it, evolutionists have completely rebuilt a look with primitive traits, which they painted alongside his wife.
In 1927 other fragments of the skeleton were discovered. It was found that it was an extinct variety of wild boar. All the graphic representations of the "Piltdown family" were quickly removed from the evolutionary literature.
Ramapithecus
In the 1930s, two fragments were discovered in India
Sure you deserve it @cristian07 . Im beginning to follow you now. Emulating you from now onward
I'm glad you loved it
Nice. There are a lot of "theories "....! Always great to listen to myth and evolution tales at the same time.
A zulu shaman talk bout this:
http://unilibrium.net/humansarefromorion.php
Hope you like it.
Hugs
There are many theories
True...and for me they are ALL TRUE! Every time used their words - every culture explained it on a different way but at the end...;-) hope to read more of ya my dear. Peace out
Thank you so much for writing this! Now I don't have to, lol. It's amazing that nearly every culture (as far as I am aware of) has an origin story of either being made or brought here, yet mainstream science and the general public just accept the idea that life randomly started in some volatile environment and then changed over the ages eventually to the point where it makes up stories about its origins, none of which include "evolution through natural selection".
Anyway, great article. Keep it up!
Thanks Rory Merrick!