Ruby Programming Tutorial - Lesson 32 - Recursion and Binary Trees
In this article we are going to learn about binary Tree data structure
Before we go learn it, we should be familiar with Recursion, and recursive methods.
so lets learn them first :)
What is Recursion ?
Recursion is a process in which a function calls itself as a subroutine. This allows the function to be repeated several times, since it calls itself during its execution. Functions that incorporate recursion are called recursive functions.
Recursion is often seen as an efficient method of programming since it requires the least amount of code to perform the necessary functions. However, recursion must be incorporated carefully, since it can lead to an infinite loop if no condition is met that will terminate the function.
Condition that makes it terminate is called "Base condition".
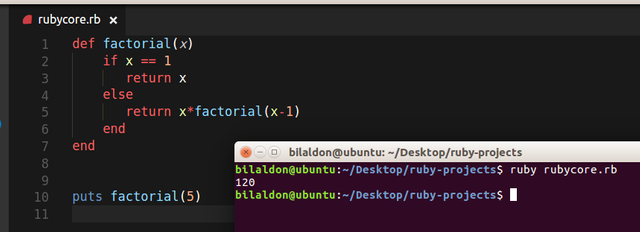
Lets have a look at a simple recursion
def factorial(x)
if x == 1
return x
else
return x*factorial(x-1)
end
end
if you will call this method
puts factorial(5)
If want to learn more about Recursion or recursive methods, search for it :) Its good idea to have a strong base on this topic before proceeding further.
Binary Trees Data Structure
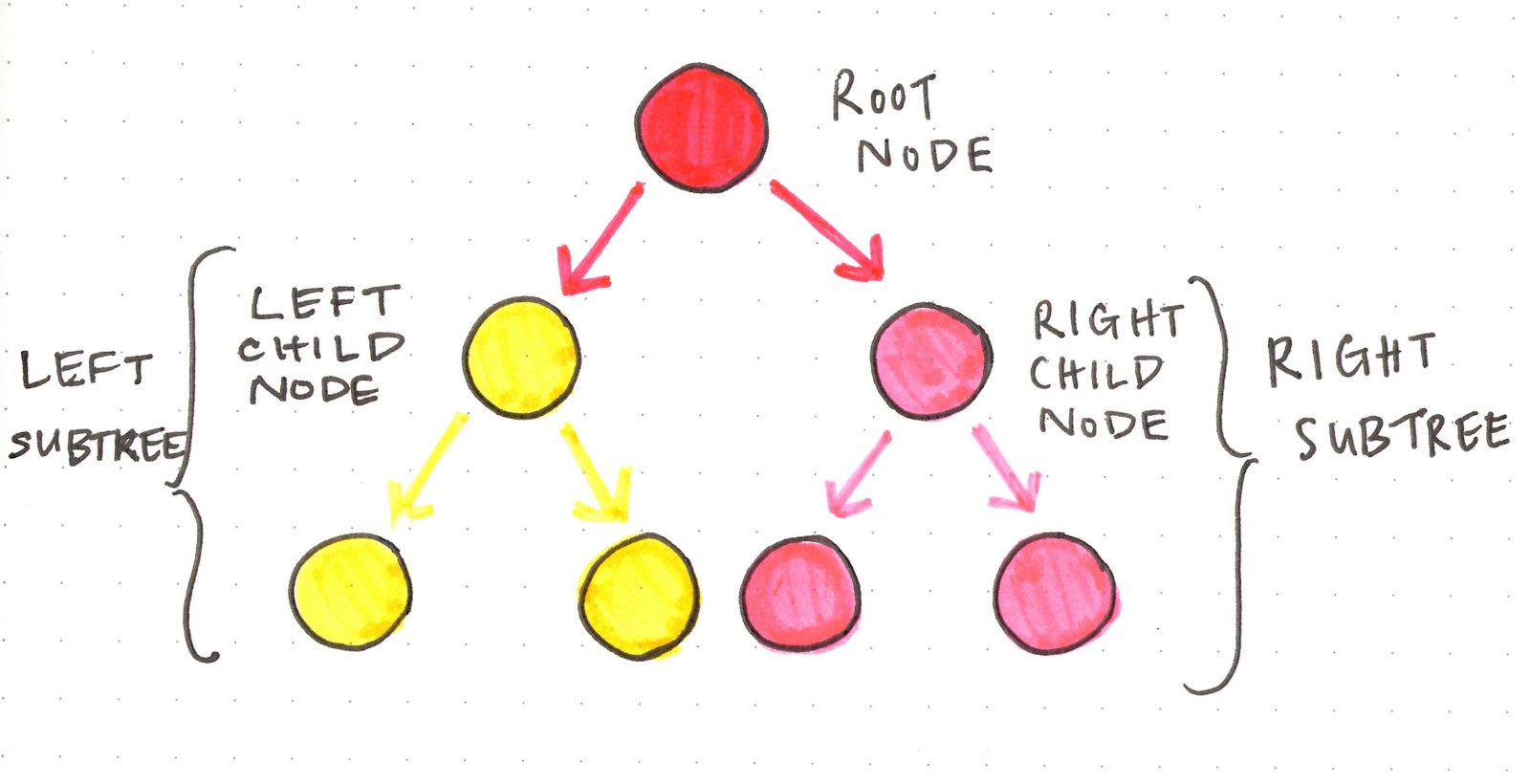
Tree is a data structure, which also consists upon nodes but nodes are connected in a way that every node has two children nodes, left and right, that is why they are called binary trees.
Each node can have 1, 2 or 0 children ..
Every Binary tree has a root node, or some people call it parent node.
Every Binary tree has leaf nodes, nodes which don't have any child nodes
Lets start by Identifying Entities
After learning about binary trees we came to conclusion that a binary tree consists upon two entities.
- Node
- Tree that consists upon nodes
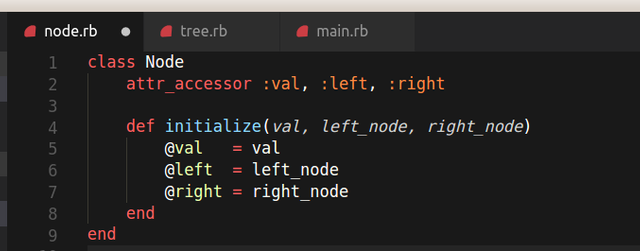
A binary tree node has three properties, it has a reference to left child, right child and a data variable
So we can create a class to represent it like so.
class Node
attr_accessor :val, :left, :right
def initialize(val, left_node, right_node)
@val = val
@left = left_node
@right = right_node
end
end
After creating Node We are ready to use it and implement Binary Tree
require_relative 'node'
class Tree
attr_accessor :root
def initialize(val)
@root = Node.new(val, nil, nil)
end
def insert_node(val, current)
puts val[:id]
if current == nil
puts "base condition"
return Node.new(val, nil, nil)
end
if val[:id] < current.val[:id]
puts "going left"
current.left = insert_node(val, current.left)
else
puts "going right"
current.right = insert_node(val, current.right)
end
end
def traverse(node)
_node = node
if(_node == nil)
return
end
puts _node.val
traverse(_node.left)
traverse(_node.right)
end
end
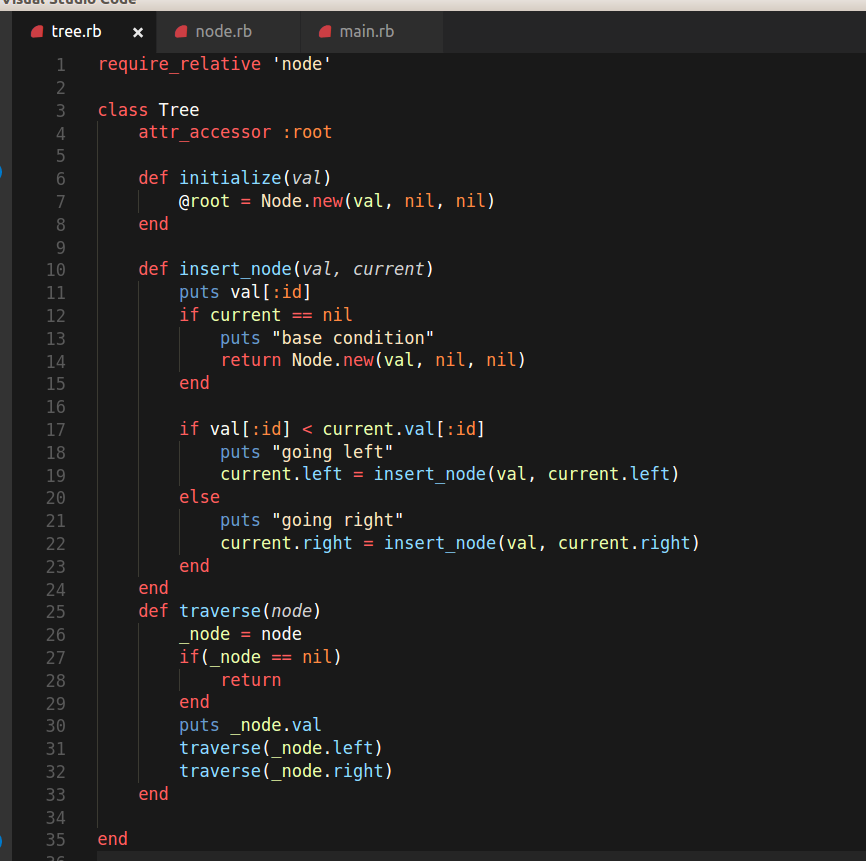
You can see that, our Binary Tree has three methods.
- initialize
- insert_node
- traverse
First method allows us to create a root node, when a tree object is created from it.
Notice that when a tree object is initialized, it creates a root node, which has no children nodes. e.g it's left and right children nodes are nil ...
lets see how we are using this Tree class in main.rb
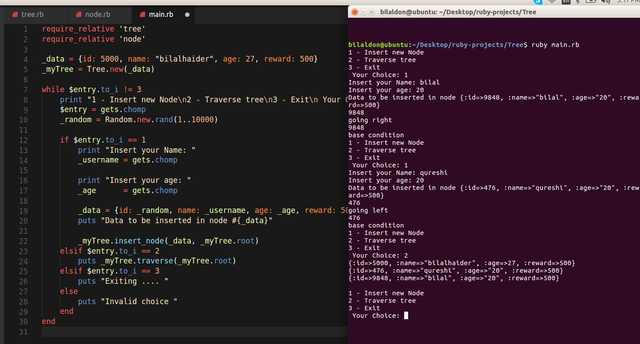
require_relative 'tree'
require_relative 'node'
_data = {id: 5000, name: "bilalhaider", age: 27, reward: 500}
_myTree = Tree.new(_data)
while $entry.to_i != 3
print "1 - Insert new Node\n2 - Traverse tree\n3 - Exit\n Your Choice: "
$entry = gets.chomp
_random = Random.new.rand(1..10000)
if $entry.to_i == 1
print "Insert your Name: "
_username = gets.chomp
print "Insert your age: "
_age = gets.chomp
_data = {id: _random, name: _username, age: _age, reward: 500}
puts "Data to be inserted in node #{_data}"
_myTree.insert_node(_data, _myTree.root)
elsif $entry.to_i == 2
puts _myTree.traverse(_myTree.root)
elsif $entry.to_i == 3
puts "Exiting .... "
else
puts "Invalid choice "
end
end
Notice that, our Second Method(insert_node) in Tree class uses Recursion, and finds perfect spot for New node, where it can be inserted.. New node that is created from user's input :)
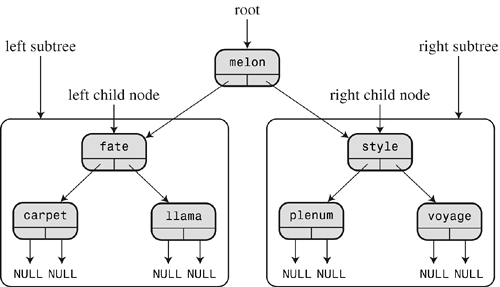
What is perfect location for a new node?
We have few rules for that .. These rules help us, later on for searching a record.
- every left node's id value is lower than its parent node's id value.
- every right node's id value is greater than its parent node's id value.
Take a look at following picture, for a better understanding :)
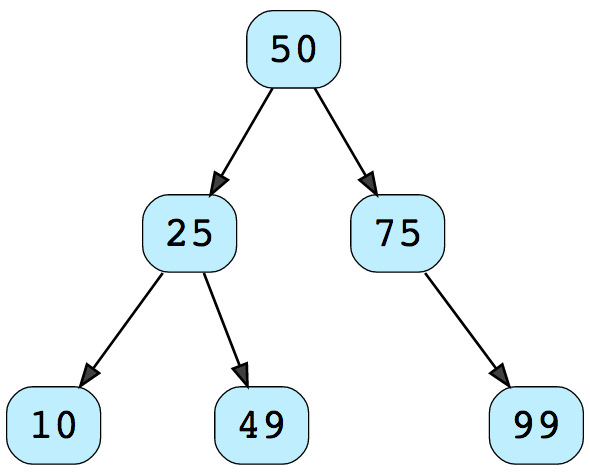
There you go my friends, you have implemented a data structure which is best when it comes to retrieving a recored of a user.
If you have 8 million records of users, it will take only 23 comparisons and you will reach your record :)
When using linked list, you may need to compare, or traverse the list and perform 8 million comparisons in its worst case to reach your record
Same number of steps required when adding a record, so binary trees will help you save time.
incredible this article. but unfortunately I do not quite understand about this encoding in this application.
I am glad you like it :)
Once again thank you for taking the time for uploading these. Keep them coming!
glad you like them :) will keep publishing more ..
Dear whqt is this and how i will learn this?
It's a smart data structure that is used to handle user's records, or big data
Oh but i tried it
Hi good post!!!