Voyager Is 13 Billion Miles Away and Needs a Repair: Here’s What Happened

Trickling in through the giant radio dishes of NASA’s Deep space community, faint whispers from a distant robot explorer supply a message: I might not have lots time left.
it is Voyager 1, our most remote explorer, nevertheless functioning and speaking with NASA because it speeds ever farther into deep area.
The message isn't a literal S.O.S. signal, however records from Voyager’s engine gadget alerting NASA engineers that a problem is on the horizon: Voyager can also soon lose the potential to align its radio dish — its verbal exchange lifeline — with Earth.
lack of contact with Voyager would spell the stop of a more than 40-12 months career of discovery, an odyssey that started with the exploration of Jupiter and Saturn and continued in a long-distance quest to find the very fringe of interstellar area.
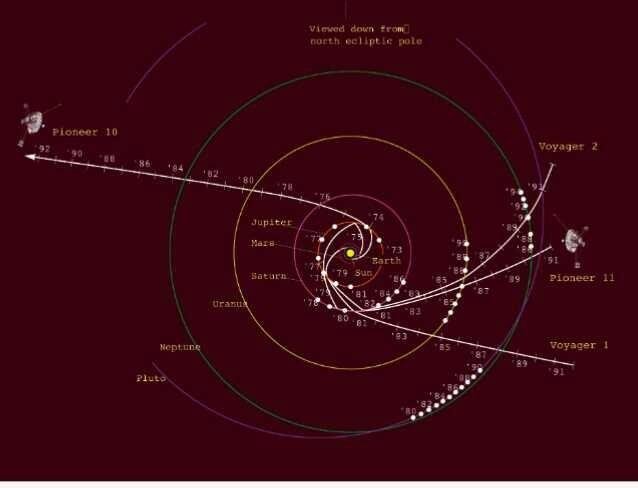
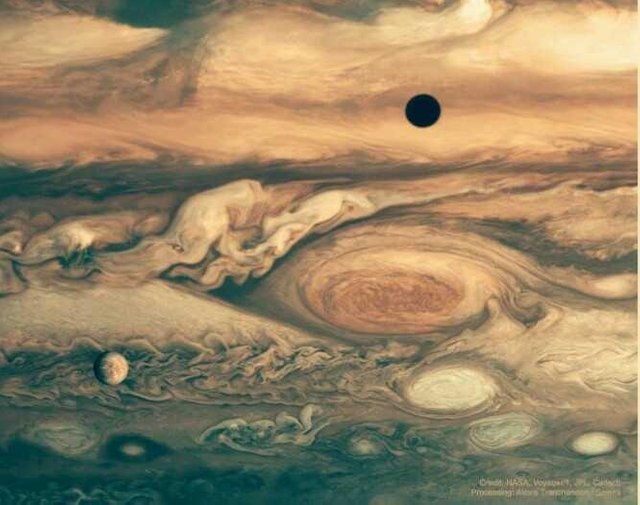
a long time ago the “grand tour” of Voyagers 1 and a couple of introduced us high-quality pictures and discoveries from Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and their moons.
They found out lively volcanoes on Io, hinted at a massive liquid-water ocean below Europa’s ice crust, and piqued our interest for Saturn’s mysterious, cloud-shrouded Titan. They showed us beautiful photos of Jupiter’s cloud belts and big hurricane systems, and opened our eyes to extraordinary information of Saturn’s jewelry.
After traveling greater than 13 billion miles, Voyager 1 has best these days crossed that threshold beyond the reach of our solar and entered interstellar area. With a enormous, unexplored realm laid out beforehand, an untimely end to Voyager’s venture now might be a splendid loss. Scientists are hungry to research extra approximately what lies between the stars of our galaxy.
Voyager 1’s test Engine light came On
It become inevitable that at some point, Voyager 1’s potential to hold in touch might begin to fade. running any such far flung area observatory presents numerous technical challenges, not the least of which is preserving radio communications over exceptional distance. NASA does this by keeping Voyager’s foremost radio dish aligned with Earth and the massive radio dishes of NASA’s Deep space community.
Left to its own inertia, the spacecraft could slowly rotate out of alignment, reacting to the subtle however persistent forces of factors like pressure from sunlight and the sun wind.
thus far, Voyager 1 has used a fixed of “mindset control thrusters” that fire in tiny bursts to subtly steer the spacecraft to hold alignment. however over the last few years, NASA has observed that these thrusters are degrading, generating much less and much less thrust and requiring longer bursts to do their process.
the way to Take A Spaceship to the Mechanic
You don’t keep using your vehicle when the engine starts offevolved to sputter, if you plan to hold riding it. you are taking it to a mechanic.
seeing that bringing Voyager in for a tune-up isn’t an option, NASA engineers needed to imagine a way to maintain Voyager’s project health using on-board resources. remember the fact that scene from Apollo 13 while the engineers needed to determine out a way for the astronauts to restore the carbon dioxide removal gadget using plastic baggage and duct tape?
The workaround for Voyager 1 become to try to reenlist a different set of engines that have been close down for 37 years.
those are Voyager’s “trajectory correction maneuver (TCM) thrusters.” They hadn’t been tested seeing that NASA engineers final used them to assist Voyager 1 maneuver through the Saturn gadget to make near flybys of the planet and its huge moon, Titan. as soon as the Saturn flyby was over, the TCM thrusters have been not wished, and have been close down.
On November 28, 2017, NASA sent the command to Voyager to check-hearth the TCM thrusters. That radio sign travelled thru space for 19.5 hours to attain Voyager (that’s now a long way away it is), even as NASA engineers waited.
Then, after every other 19.5 hours of silence, NASA’s Goldstone radio antenna in the Mojave desert obtained word from Voyager 1 that the thrusters had fired!
NASA now has a route ahead to preserve Voyager 1’s communication dish going through Earth for as a minimum some other or three years, by using switching to the TCM machine as soon as the modern-day thrusters have gone off-line.
The Voyager Legacy
launched in 1977, Voyager 1’s number one assignment turned into to make flybys of the Jupiter and Saturn systems before being flung with the aid of Saturn’s gravity onto a course that might take it out of the sun machine, certain for interstellar space.
Now, Voyager 1 is the maximum remote human-made object from Earth, and has been since it overtook the venerable Pioneer 10 in 1998. As of March 2018, Voyager 1 is over 13 billion miles away—or 141 instances further from the sun than Earth is.