The blood is the most important fluid in the body, no traditional body fluid is actually of less importance, but the blood gets a higher rank when compared on a physiological basis. From a simplified view, the blood is a suspension of cells on a fluid medium known as the plasma. The plasma itself is a fluid of about 90% water and a solution of other organic and inorganic substances. Digested forms of the food we eat such as amino acids, monosaccharides and fatty acids constitutes the organic suspensions of the plasma, vital body proteins such as fibrinogen and other coagulation factors also makes up this class. The inorganic solvents dissolved in the plasma are mainly ions in the form of such as zinc, copper, iron and a host of other ions which constitutes the vitamins and minerals. Hormones are also suspended on the plasma in the course of its transport to the target organs.
These suspensions and solutions are much needed and are meant to be transported to their target organs where they are utilized to maintain a constant internal body conditions amidst the ever changing external conditions, wastes of metabolism such as carbondioxide are also transported to the lungs via the blood where they are exchanged with the much needed oxygen to continue external and internal respiration. The cells suspended on the fluid part of the blood are the blood cells, leukocytes, erythrocytes and the thrombocytes commonly known as the red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets respectively, their vitality to the body is unarguable.
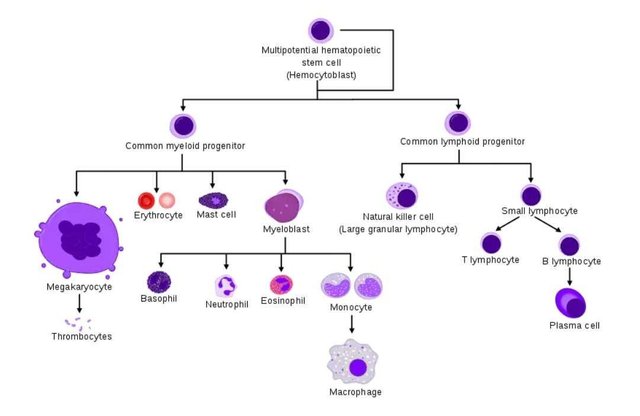
the blood cells . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
While the erythrocytes binds and transports oxygen, the white blood cells are the main arm of the body’s immune system and the platelets ensures the integrity of the blood vessels by maintaining the blood flow through the covering of little and noticeable openings in the blood vessels as the blood moves round the body due to physical injuries or other defects which traumatizes the blood vessels, hence if the body must continue in normal function, the dynamics, kinetics, the presence and normal functioning of these cells and molecules are indispensable.
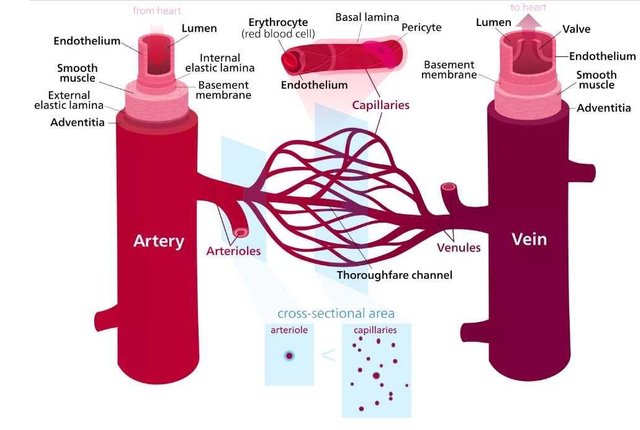
blood vessels circulates blood throughout the body . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
To every body system is a circulatory system which blood is the chief circulating fluid which moves through carefully crafted vessels which are distributed all over to meet the demands of each organ, tissues and cells which are in turn dependent on their metabolic capabilities and their rate and intensity of their metabolism. The brain, liver and kidneys are highly active and this accounts for the conspicuous focus on them by the circulatory system, these organs have the greatest concentration of blood vessels around and within them, even in pathological conditions, the blood flow to other parts of the body is occluded so as to meet the requirements of these organs as the body can’t survive their inconsistency in action.
This professional circulation scheme is not seen in lower animals such as the grasshoppers whose blood doesn’t flow in vessels but are housed in a chamber known as Haemocoel where the body organs are washed and in the process, needed exchanges occurs, this is a form of open circulation as compared to the circulation in the human body referred to as closed circulation.
The human body is not a plain structure, even if it was to be plain, humans are vertical in stature or a little bit oblique, but certainly not horizontal, even while lying horizontally, the whole body parts are not tandem and hence a pronounced elevations and depressions which are not arranged in a uniform interval exists in the course of the body contour, in these unarranged and rugged elevations and depressions are located some vital organs, systems and tissues which requires continuous flow of blood, thus for blood to get to these organs, there’s the need for flow under pressure so as to enable the fluid move across the gradients to get to these organs in question.
Pressure can be provided in nature by gravity, even in pathological conditions such as edema, serum (a plasma which lacks fibrinogen and blood clotting factors) accumulates at the extremities as they are forced down this location by gravity. But gravity would certainly not be able to power the flow of blood inside the body system as it acts vertically and not horizontally too, thus the need for a pumping system which would provide adequate force to move the blood through the vessels to the body cells and organs in a well specified manner to meet up with these varying need for blood at different conditions, locations and positions. Blood circulation is also a continuous process and any break in circulation at any time or place will result in severe damages to the whole body and not the affected organ alone, as a result, this pumping organ has to work continuously and in normal state to ensure that the body continues in healthy function.
The tireless pump
Mammals and other high animals have evolved an organ known as the **HEART** which meets these specifications as required by the circulatory system.
While the brain is regarded as the articulation centre of the human body system, the heart is the engine of the body system, just like power source to a desktop computer’s central processing unit and every other part of the computer, the heart powers the activities of every other part of the body. Apart from the anatomy discipline, a symbol of the heart has also been used to represent vitality, value and importance, all summarized in the word **’love’**.

Its not love! It's just my heart! . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
We use a symbol of the heart to represent our love for people, something, somewhere and even a phenomenon amidst the fact that love is a psychological condition /state and does not in anyway come from the heart but from the brain which is our articulation unit. The heart performs a function which is completely different from articulation or cognition, *completely* may seem too absolute to use but from a basic view, this is the right word which qualifies the difference between the function of the heart when compared to the brain. Even the cognitive ability of the heart is linked to the nervous system which actually does the job and the heart is only a channel for relays and effection via the afferent and efferent nerves respectively, this is also seen in every other part of the body which is not a traditional part of the nervous system.
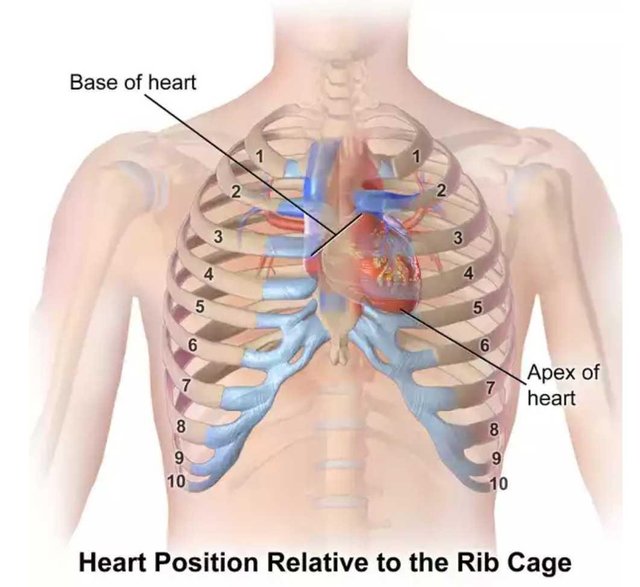
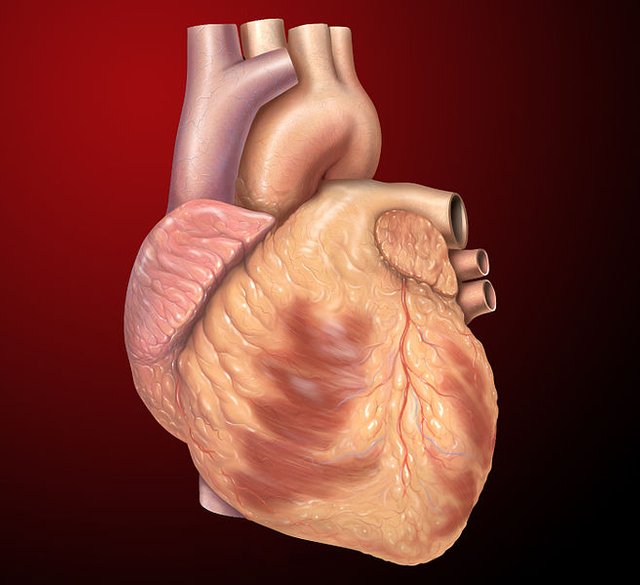
The heart housed by the thoracic cavity . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
The human heart is a vital organ, and just as most other vital organs in the body, the heart is positioned in a way to keep it safe. The thoracic cavity (also known as the mediastinum) houses the human heart, it is located between the first and twelfth thoracic vertebrae (T1-T12), equipped with twelve pairs of specially constructed flat and flexible bones known as ribs which are joined to the sternum, the thoracic cavity houses many other vital organs which includes the lungs and many important vessels of the body such as the aorta and Vena cava, this proximity between the heart and these organs also simplfies the functioning of the heart
The sternum at birth is a piece of cartillage which ossifies at about the age of twenty-five (25), the ribs ossifies about five years earlier, hence the thoracic cavity cavity is not a box of bones until about the age of twenty-six (26). Even before this time, the thoracic cavity is strong enough to protect the human heart from moderate external attacks and as a result, most heart problems emanate from internal abnormalities. A horizontal plane through the angle of the sternum divides the thoracic cavity into four compartments named according to their positions as superior, middle, anterior and posterior mediastinum, these divisions also contains different organs. While the superior mediastinum contains the ‘great’ vessels,( aorta and vena cava), phrenic nerves, vagus nerves and trachea; the anterior mediastinum contains the thymus, the posterior mediastinum contains the oesopahagus, veins and the thoracic duct.
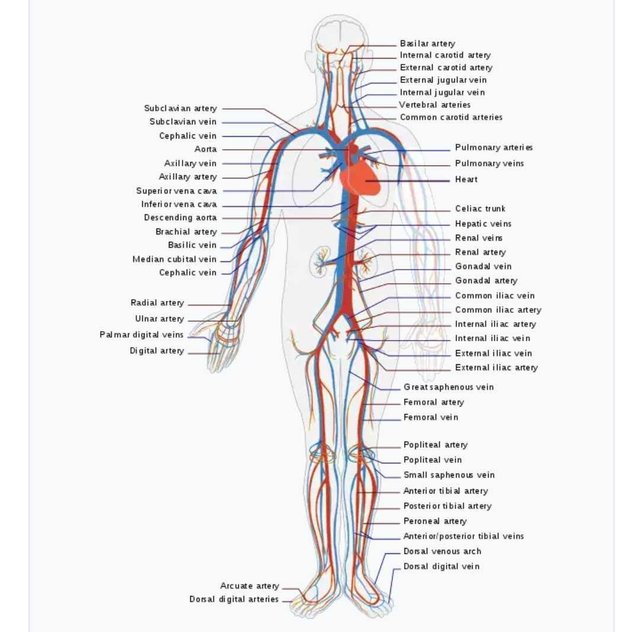
The circulatory system . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
The heart is located at the middle mediastinum and it’s coverings the **pericardium**, and the cardiac plexus. Just a little bit of anatomy; The four chambered organ lies obliquely in the thorax with it’s axis passing downwards and to the left of the apex, the chambers of the heart does not actually lie as their name implies, the right chambers are actually anterior to the left chamber and the atria which are supposed to lie superior to the ventricles are actually at the right side of their respective ventricles, these chambers are equipped with valves which opens in response to pressure emanating from the heart muscles, the opening and closure of the heart valves also adds pressure to the blood flow and transport, the tricuspid valve and mitral valve in the right and left chambers of the heart separates the auricles from the ventricles, an interatrial septum also separates the atria and these ensures that blood flows in compartments and to the right vessels for general circulation or oxygenation. The pulmonary vessels are in charge of the oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange, while the aorta moves blood away from the heart, the vena cava returns blood from general circulation for oxygenation through the lungs. The coronary arteries supplies the heart with blood.
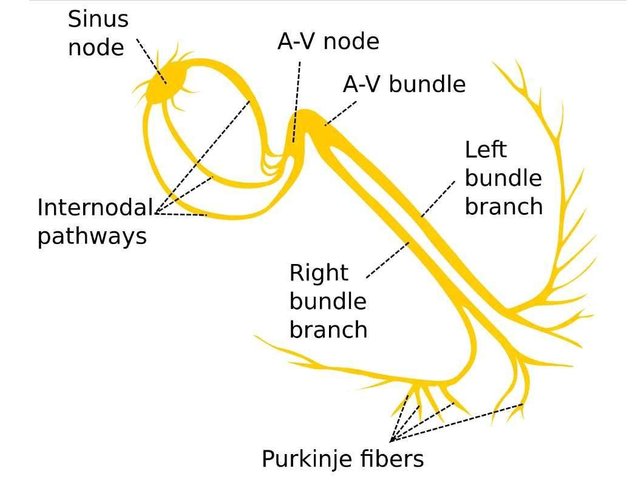
The electrical conduction system of the heart . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
The pumping action of the heart is enabled by some very special electrical activities which is more explained in the electrocardiogram. The cardiac muscles are striated involuntary muscles with large numbers of elongated mitochondria which are in close contact with the muscle fibres and supplies the much needed energy for the actions of these muscles, the muscle fibres are well covered by cell membranes and these muscles interdigitate, each lying end to end with one another and the fibres lying parallel to each other. An **Intercalated disc** lies between these parallel muscle fibres and creates a reliable connection between them, maintaining cell to cell cohesion so that contraction in one muscle unit can be transmitted along the next fibre. Gap junctions are also formed by the fusion of the cell membranes of adjacent muscle fibres and provide low resistance bridges for the spread of electrical excitation from one fibre to another thus permits the cardiac muscle system to function as a syncytium.
The contractile response of the cardiac muscles begins just after the depolarization, these contractions are the source of the Heart beats which is a means of rating the cardiac function. This beats originates in a special conduction system to all parts of the cardiac muscles. The myocardial conduction system consists of the Sino atrial node, atrioventricular node and an internodal atrial pathway between them, the bundle of His and it’s branches and the purkinje system. These systems are capable of spontaneous discharge of contractions at different speeds to enable the functioning of the heart. The Sino atrial node transmits contractions fastest at 72 times per minute thus it spreads the contractile impulse through the entire system before other parts are able to discharge their impulses, hence dubbed the cardiac peacemaker. These contractions are in response to the changing membrane potentials of the cardiac muscle cells.
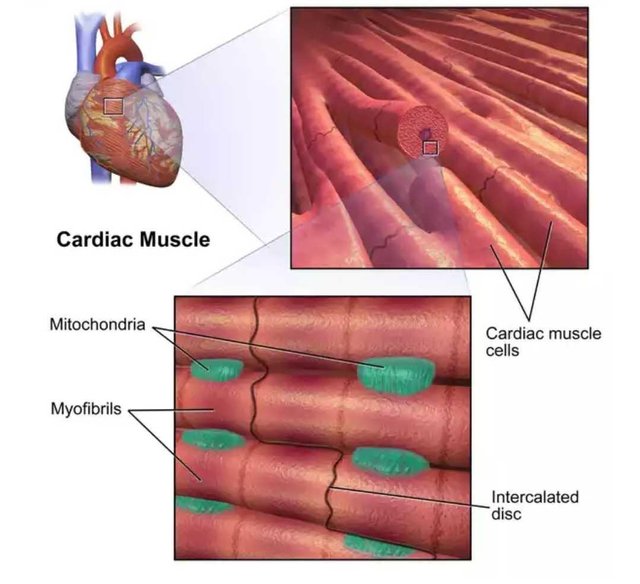
The cardiac muscle. Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
The resting membrane of the individual cardiac muscle cells is about -90mV, the auto-rhythmic cells of the cardiac conducting system have an unstable resting membrane potential that continuously depolarizes, these spontaneously changing membrane potentials are known as the *prepotentials*. Depolarization of the cardiac muscle cells proceeds rapidly and an overshoot is present, but is followed by a plateau before the membrane potential returns to the baseline. Depolarization lasts for about two milliseconds (2ms), this begins as a result of decrease in potassium ion (k+) efflux and calcium ion influx through the transient calcium channels, the action potentials in the Sino artrial and Atrioventricular nodes are largely due to calcium ion influx, the effects of sodium ion (Na+) influx in cardiac muscle cells depolarization is undetected. The depolarization of the heart supplies the systolic blood pressure.
Repolarization follows after depolarization, the plateau phase and repolarization lasts about 200 milliseconds (200ms), this occurs as a result of opening of the k+ channels and increased k+ efflux from the channels, repolarization lasts until the contraction is over. Repolarization of the heart supplies the diastolic pressure.
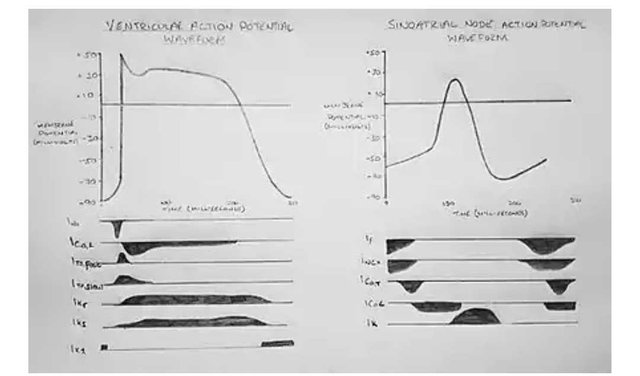
cardiac action potential . Source:Wikimedia - CC BY-SA 3.0.
These electrical activities brings about the heartbeats and provides the much needed pressure to move the blood through the body, blood in the artery flows with a higher pressure than that in the veins. The heart not only provides pressure for blood circulation, it also aids the oxygenation of the blood and excretion of carbon dioxide. The normal blood pressure is 120mmHg/80mmHg systolic and diastolic pressure respectively, though variations of about 110-129mmHg systolic pressure and 70-89mmHg diastolic pressures are considered physiological, variations due to age, location and physical state may exist. Pathological increase to about 160/90mmHg is a symptom of hypertension which may be due renal dysfunction, endocrine disorders such as hyperaldosteronism, constriction of the aorta or increased peripheral resistance. Increased blood pressure has also been reported in pregnancies, this is believed to be caused by polypeptide vasoconstrictors secreted by the placenta.
We shall discuss the electrical activities of the heart as displayed by the electrocardiogram on the next part of this article.
References
Review of medical physiology by William Ganong
The functions of the heart~ivyroses
Heart~wikipedia
If you write STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) related posts, consider joining #steemSTEM on steemit chat or discord here. If you are from Nigeria, you may want to include the #stemng tag in your post. You can visit this blog by @stemng for more details. You can also check this blog post by @steemstem here and this guidelines here for help on how to be a member of @steemstem. Please also check this blog post from @steemstem on proper use of images devoid of copyright issues here.










Interesting topic. I would like to point out that several words are not bold or italic as you wish. Maybe some problems with the Markdown coding?
There seems to be a lot of terminologies that a layman would be confused about. Good luck with your next article about ECG. It will be tough but if you can make it simple and concise, you are the man.
It appeared well on the esteem app, can't tell why it didn't appear so on other browsers.
Thanks a lot for pointing it out, tried some editing but the problem still persists, I guess its from the app
Hello! I find your post valuable for the wafrica community! Thanks for the great post! We encourage and support quality contents and projects from the West African region.
Do you have a suggestion, concern or want to appear as a guest author on WAfrica, join our discord server and discuss with a member of our curation team.
Don't forget to join us every Sunday by 20:30GMT for our Sunday WAFRO party on our discord channel. Thank you.
Congratulations, your post has been featured in today's selections for @wafrica posts of the day. Keep contributing quality content to the Steemit community.
@lordjames...
This post has been voted on by the steemstem curation team and voting trail.
There is more to SteemSTEM than just writing posts, check here for some more tips on being a community member. You can also join our discord here to get to know the rest of the community!