Before THE BIG BANG | Ch 7. JAMES WEBB Space Telescope

Hey Starlord here,
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope developed in collaboration between NASA, the European Space Agency, and the Canadian Space Agency.
One of its major goal is observing some of the most distant events and objects in the universe, such as the formation of the first galaxies. These types of targets are beyond the reach of current ground and space-based instruments. Other goals include understanding the formation of stars and planets, and direct imaging of exoplanets and Nova.
The telescope is named after James E. Webb, the American government Official who was the administrator of NASA from 1961 to 1968 and played an integral role in the Apollo program. The project has had numerous delays and cost overruns and underwent a major redesign during 2005.
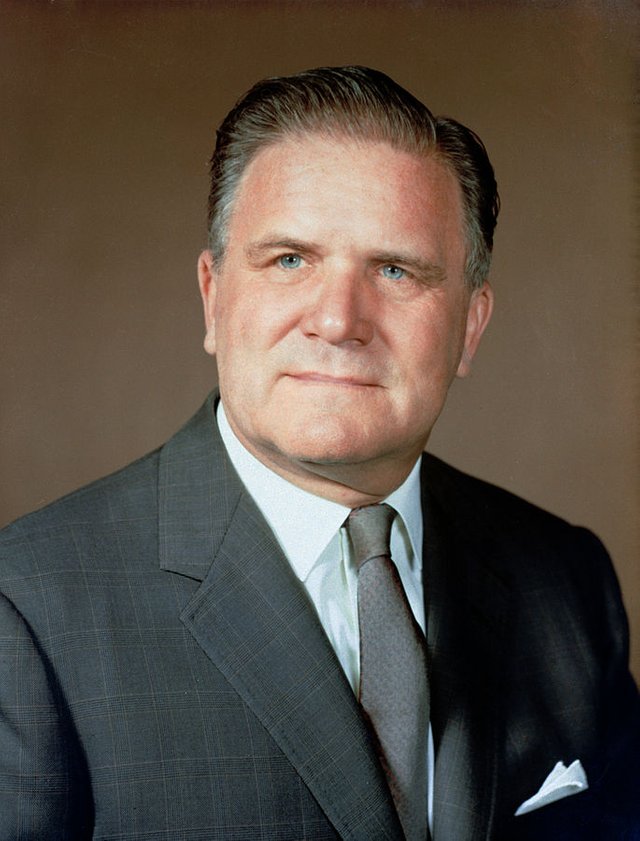

[James E. Webb, Administrator. NASA HDQS., WASHINGTON, DC B&W]
In December 2016, NASA announced that construction of the JWST was complete and that its extensive testing phase would begin. In March 2018, NASA delayed the JWST’s launch after the telescope’s sunshield ripped during a practice deployment and the sunshield’s cables did not sufficiently tighten.
In June 2018, following recommendation from an independent review board, the JWST’s launch was delayed again, and is currently scheduled for 30 March 2021.
This telescope will give unprecedent ability to see way back to the very early universe and observe the formation of the very oldest galaxies. Webb will allow us to unlock secrets of the beginning of space and time…
The Webb telescope will capture long-travelling light to see the universe’s infancy, early stars and galaxies flickering to life after the Big Bang. It will investigate why galaxies produced stars so much faster in the past; 10 Billion years ago, the rate of star birth was 10 times higher.
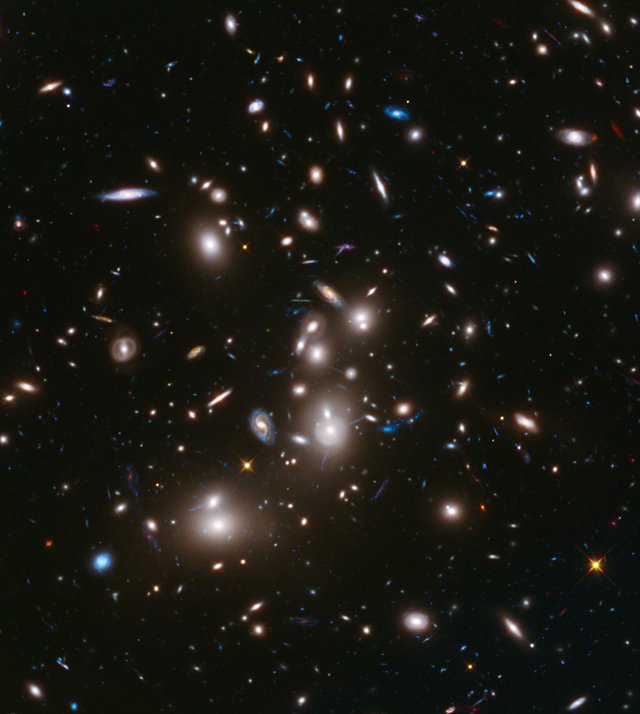

Galaxy clusters like Abell 2744 can act as a natural cosmic lens, magnifying light from more distant, background objects through gravity. NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope may be able to detect light from the first stars in the universe if they are gravitationally lensed by such clusters.
Credits: NASA, ESA, and J. Lotz, M. Mountain, A. Koekemoer, and the HFF Team (STScI)
We’re accustomed to seeing stately spiral and shining elliptical galaxies, but we don’t know how groups of stars evolved into these familiar shapes. Webb will uncover whether the process is something internal to galaxies or affected by outside events, such as galaxy collisions. ref
Shortly after the Big Bang, the universe went through a period known as dark ages, where no light sources were available. Webb will look for the bright objects that transformed this dark universe to the one we see today, ablaze with the glow of stars, gathered into immense galaxies.
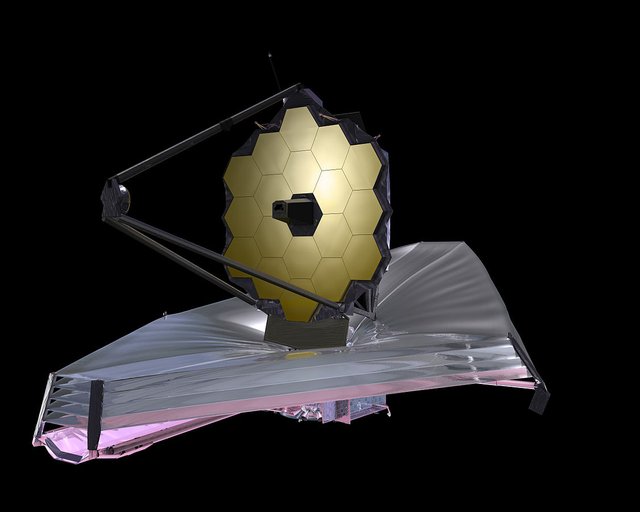
By NASA (direct link), Public Domain,wikimedia
Webb will see the first, tiniest galaxies of the cosmos, and witness their evolution vast islands of stars.
Webb will monitor the weather and atmosphere of the giant planets and study the composition of smaller objects in our solar system.
Webb will search for signs of life-sustaining water on planets beyond our solar system and help us to learn how planets form.
Webb will be stationed at the second Sun-Earth Lagrange point(L2), an orbit beyond the Moon, further than humans Have ever travelled.
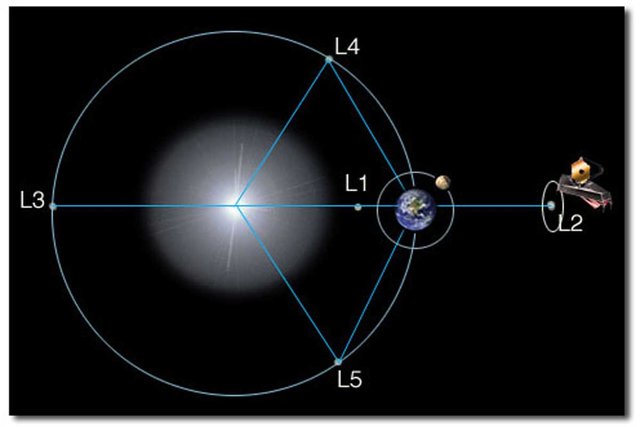
[The five Lagrangian points for the Sun-Earth system are shown in the diagram below. An object placed at any one of these 5 points will stay in place relative to the other two. Credit: NASA]
Webb’s giant sunshield will protect it from stray heat and light, while its large mirror enables it to effectively capture infrared light, bringing us the clearest picture ever of space objects that emit this invisible radiation beyond the red end of the visible spectrum early galaxies, infant stars, clouds of gases and dust, and much more.ref
With ground-breaking design and technology, the Webb telescope will breach the veil of the unseen universe.
Webb will also look at the condition of water on Mars and how they relate to the planet’s potentially habitable past and present.ref It will map organic molecules on Uranus and Neptune, revealing information on the chemistry of those planets.
And with its high-resolution and light-analysing spectroscopy instruments, Webb will be able to tell us more about smaller bodies like dwarf planets and asteroids.
Thanks for reading and learning
refrences for further reading
- Official website
- The James Webb Space Telescope will bring us closer to a galaxy far, far away
- JWST factsheet
All images are CC Licensed and are linked to their sources
I upvoted your post.
Best regards,
@Council
Posted using https://Steeming.com condenser site.
Congratulations! This post has been upvoted from the communal account, @minnowsupport, by starlord6414 from the Minnow Support Project. It's a witness project run by aggroed, ausbitbank, teamsteem, someguy123, neoxian, followbtcnews, and netuoso. The goal is to help Steemit grow by supporting Minnows. Please find us at the Peace, Abundance, and Liberty Network (PALnet) Discord Channel. It's a completely public and open space to all members of the Steemit community who voluntarily choose to be there.
If you would like to delegate to the Minnow Support Project you can do so by clicking on the following links: 50SP, 100SP, 250SP, 500SP, 1000SP, 5000SP.
Be sure to leave at least 50SP undelegated on your account.
Congratulations @starlord6414! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Click on the badge to view your Board of Honor.
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP