How Can We Cure Aging?!

Health is one of the most valuable things we have in life, but we tend to forget that until we lose it.
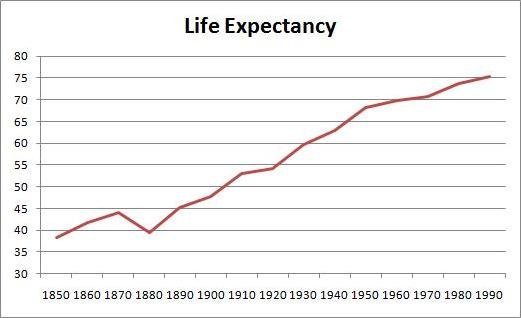
Nowadays we're living way longer than ever before. Getting old currently means spending more time in pain.
So scientists are trying to shift the attention of the medical community from optimizing lifespans to optimizing healthspans. The part of our lives during which we're disease free.
To do this, we need to find and attack the root case of almost all bodily defects.
Unknown to most people, the science of aging has made enormous progress in the last few years, with human trials about to begin in the near future.
There are three examples of discoveries that might benefit people who are alive right now.
Senescent Cells
All cells have an expiration date. Each time one of our cells divides, it copies its chromosomes.
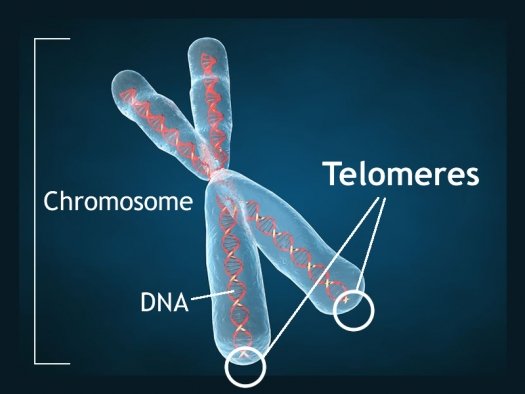
Because of the way this works, they lose a tiny bit of DNA at the ends. This could be catastrophic, so to protect themselves we have long segments of DNA called telomeres. However they shrink with every cell division.
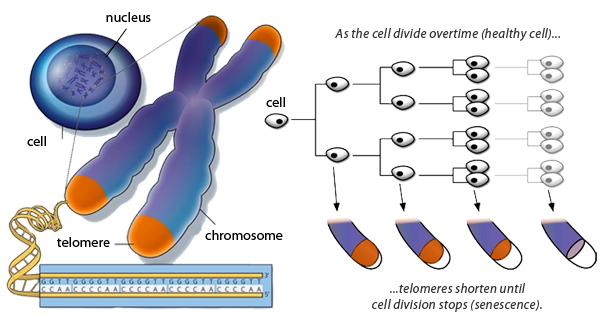
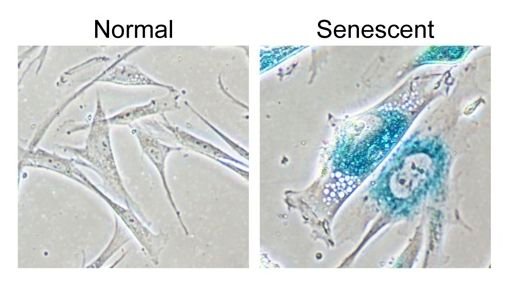
In some cells, after a number of divisions the telomeres are gone, and the cell becomes a senescent cell.
Senescent cells stay around and don't die. The older you get the more of them are inside you.
They harm tissue around them and are linked to many diseases that accompany old age, like diabetes and kidney failure.
Scientists genetically engineered mice so that they could destroy their senescent cells as they pleased.

Older mice without senescent cells were more active. Their hearts and kidneys worked better, and they were less prone to cancer. They lived up to 30% longer and in better health than average mice.
Most cells in the body commit a programmed cell suicide when they're damaged, but senescent cells don't.
It turns out that they underproduce a protein that tells them when it is time to die.
In a late 2016 study, mice were give an injection of this protein. It killed 80% of all their senescent cells , while causing almost no harm to healthy cells. The treated mice became generally healthier and even regrew lost hair.
There are a number of new companies looking at treatments involving senescent cells and the first human trials will start soon.
NAD+
Cells are made from hundreds of millions of components, they are the structures, machines, messages, and the catalysts that make reactions happen. All these parts constantly need to be destroyed, cleaned up, and rebuilt.
As we age, this process becomes less and less effective and so parts become crumpled, bunched up or are removed slower, or they are no longer produced in the quantities we need.
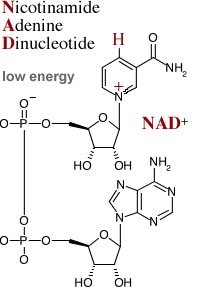
One of these parts is NAD+, a coenzyme that tells our cells to look after themselves.
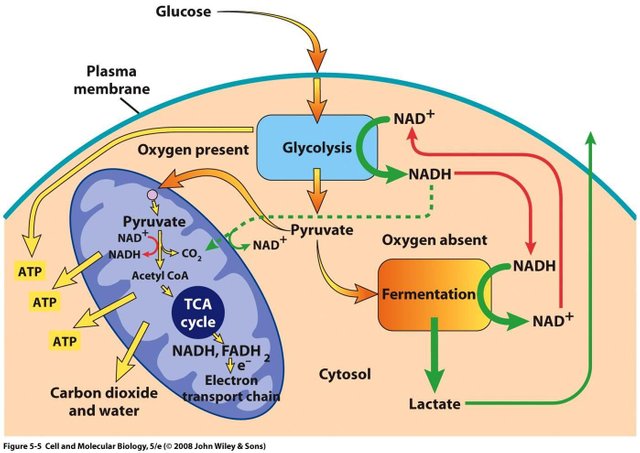
At age 50, we only have about the half as much in our bodies as we do at age 20.
Low amounts of it are linked to a whole bunch of diseases from skin cancer to Alzheimer's, cardiovascular disease and multiple sclerosis.
NAD+ is a big molecule it can't enter cells so we can't use it as a pill or an injection.
Scientists notice that other precursors, more flexible than NAD+ could enter cells and would then turn into NAD+ inside.
In 2016, multiple trials on mice showed that they boosted multiplications on skin, brain and muscle stem cells.
They were rejuvenated, had a higher ability to repair their DNA, and had a slightly increased lifespan.
There are human trials being planned right now. However it is too soon to say if this will boos our healthspan or even lifespan. NAD+ could become the first anti-aging pill.
Stem Cells
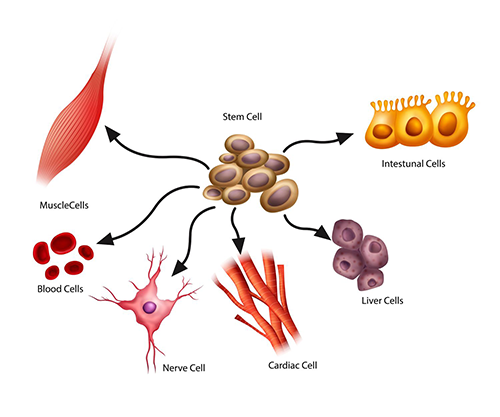
Stem Cells are like cell blueprints that sit at various places in the body and copy themselves to produce a steady flow of fresh young cells, but they decline as we age so we decline too. And without new parts human bodies deteriorate.
In mice, scientists observed that as the stem cells in their brains disappeared, they started to develop diseases.
So they too stem cells from baby mice brains and injected them directly into the brains of middle-aged mice, into the hypothalamus, a polyp that's involved in regulating a lot of body functions.
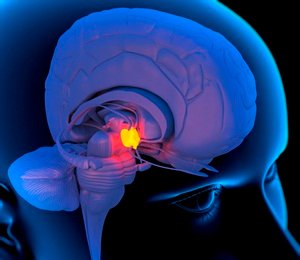
The fresh stem cells reinvigorated older brain cells by secreting micro RNAs that regulated their metabolism.
After four months, brain and muscles worked better than those of untreated mice and on average, they lived 10 percent longer.
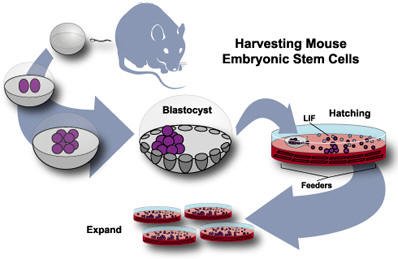
Another study took stem cells from mice embryos and injected them directly into the hearts of older mice.
As a consequence, they had improved heart function, could exercise 20% longer, and weirdly enough their hair regrew faster.
|
There is no single magic method with which to cure aging. It requires a complex array of different therapies.

This monument "symbolizes gratitude for the animal that humanity has used to study genetics, molecular and physical mechanisms of diseases, as well as for the development of new drugs." And it is located in Novosibirsk, Russia.
Thanks for reading! Feel free to follow, vote and Re-esteem if you find it useful. You can find more of my articles here:https://steemit.com/@sungazer13
Cool I really like it
Resteemed to over 5700 followers and 100% upvoted. Thank you for using my service!
Send 0.100 Steem or 0.100 Steem Dollar and the URL in the memo to use the bot.
Read here how the bot from Berlin works.
@resteem.bot
Thanks for reading, and commenting!!