Let's Make it Clear: What is the consensus and what kinds exist? (Detailed explanation)
An overview of different algorithms - validation of transactions
Image source: CoinCentral
Often in cryptocurrences you encounter different terms, but something that each one has to have is the algorithm that achieves consensus. There are different types of these algorithms, most commonly referred to as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. The purpose of this article is to clarify these terms, which differ and what are the advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
A consensus or agreeing unanimous decision is a decision-making process that is not based on "majority rule" but at the highest possible consensus within the group. In the world of cryptocurrencies, the concept of consensus refers to the principle of transaction verification. Consensus is a method that differs from the correct "false", malicious transactions.
There are several methods to achieve consensus. The most common method is the Proof of Work. Proof of work is the most widely used method of consensus, and is actually related to mining. Also popular is the new method of the machine, Proof of Stake - a proof of the role. There are a number of methods each of which has its advantages and disadvantages, we will try to clarify in a shorter overview how they are different.
PROOF OF WORK (PoW, Mining)

Image source: Pixabay
Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, Dogecoin, ...
🍀Advantages:
- The only factor in the production of new money in circulation is the external factor - electricity and hardware equipment.
- Anyone can mine these cryptocurrencies
- Favorable for the parts of a lot of unused el. energy or a lot of natural energy sources (China, Islandia)
🍁Disadvantages:
- The network is slow when used by a large number of users, i.e. it is not suitable on global range
- Mining is profitable only with the use of professional equipment and specialized processors and graphics cards
- High energy consumption, environmentally unacceptable. Increase in electricity may undermine the existence of cryptocurrencies
Proof of Work is the first designed algorithm to reach a consensus. Developed by Satoshi Nakamoto, the creator of Bitcoin. This term is in fact identical to the notion of mining. PoW (or mining) is a process in which computers called miners need to solve complex mathematical problems. After solving the problem, they are rewarded with a certain amount of cryptocurrency that they mine. They use large amounts of electricity when mining because of the usage of processors or graphics cards. Then based on the difference of the obtained value of the cryptocurrency - (electricity consumption + equipment) is calculated profit.
After the miners resolve the task, in addition to receiving the amount of cryptocurrency, a new block and the corresponding transaction are added to the existing blockchain. PoW is based on the system "longest chain wins". Since all the miners are on the same chain, when the attacker attempts to set a "fake" block, a new chain is created. Then it decides which chain is the "real" one. This means that this is the chain in which the creation has invested at least 51% of the total computing power used for the hashing power. That is why it says that the Bitcoin network is safe as long as 51% of power is not in the hands of a one man or a small group of people.
The complexity of tasks increases during mining, more and more. Energy is needed for mining blocks. All this electricity is actually spent on meaningless calculations, and enough to tell us that the Bitcoin size network consumes more electricity a day than the whole Singapore. This is extremely ecologically unfavorable, so more and more cryptocurrencies are leaving this method of achieving consensus. Even the second most popular cryptocurrency, Ethereum, migrates to a more cost-effective and more economical Proof of Stake.
PROOF OF STAKE (PoS)

Image source: UseTheBitcoin.com
Proof of Stake (PoS) is completely different from the Proof of Work. Instead of creating new blocks based on computer work, the creator of the block is determined by the share of money in the account - stake.
Cryptocurrencies: Cardano, Peercoin, QTUM, OmiseGo, and soon Ethereum…
🍀Advantages:
- Fast transaction processing and higher scalability
- It does not require a great expense of el. energy - environmentally acceptable
- It does not require special equipment, ie demanding hardware
🍁Disadvantages:
- Rich are getting richer, only a small number of users can participate
- It can bring together groups of people who have the highest share of cryptocurrencies
- Nothing at Stake Problem - In the case of a fork network, validators can validate both blockchains because that way they win for shure
In this system, the creators (PoS Equivalent to the Miner) are selected to create blocks based on their role of currency and the age of that role within the network. In other words, in the PoS system, the block creator, ie the one that verifies transactions is determined based on the 2 parameters: how much money is in the account and how long.
Example: OmiseGo is one of the cryptocurrencies that uses PoS. Let's say you have 20,000 OMGs in your account. Then you are more likely to be chosen as the creator of blocks compared to someone who has 5,000 OMGs. Also, it is even more likely if you have these 20,000 OMGs in your account for a year.
Image source: CoinCentral
It is a system in which rich people are getting richer. How you can get rich? Each transaction has a commission. When you are selected as a Block Maker in a PoS system, the commission of each transaction you confirm goes to your account. There is also no prize for creating a block, as in the PoW system described earlier.
Since there is no need to deal with difficult tasks in such system, there is no need for some special equipment such as mining. Transactions are confirmed much faster and there is not much spending of energy.
The PoS system is also very secure because if the selected block creator, ie the transaction validator becomes malicious, ie attempts to validate "false" transactions, then risks all his stake. Also, such malicious behavior risks not only its stake, but also the value of the currency, because it loses a lot at every drop in prices that may cause such behavior. In order for the attacker to take control over the net, ie to reach 51% of the attack mentioned earlier, he should be the owner of 51% of that cryptocurrency. Also, then it would be illogical to expect anyone to try to manipulate the currency by risking the value and exposing the biggest loss.
PoS seems to be a much better solution than the PoW, achieving a high level of security while simultaneously solving the concept of scalability.
DELEGATED PROOF OF STAKE (DPoS)

Image source: DistributedLab
Cryptocurrencies: BitShares, Steem, EOS, Lisk, ARK…
🍀Advantages:
- Fast transaction processing, can withstand the heavy load of the network
- Any irregularity in the network is detected within 1-2 minutes
- All network users have the right to decide who will become a delegate, the system is partly centralized but with great domination of democracy
- Like PoS, it's ecologically acceptable
🍁Disadvantages:
- Delegates can join in groups that are then manipulating the network
- Because of the smaller number of responsible people, it is theoretically easier to perform 51% of the attack on the network, but such a situation has not yet occurred
Blockchain engineer Daniel Larimer realized that bitcoin mining was unreasonably energy-consuming. He also recognized Bitcoin mining will become centralized in the future, where several large mining pools control Bitcoin's network. Larimer wanted to create a system capable of achieving transaction speeds like 100,000 transactions per second. Bitcoin based on the way of achieving consensus (PoW) could not leave such characteristics.
So, in early April 2014, he published a scientific paper explaining the new system that uses little el. energy, fast and secure - Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS).
With the DPoS system, the entire community selects 20-101 delegates, computers that serve as transaction validators. They are paid on commission basis for their work. These delegates are selected based on voting, which is actually always active, ie ongoing. Anyone who has some cryptocurrencies of this system in his wallet has the right to vote. But "weight," the importance of the voice is not the same among users. The importance of vote is greater for those who have a larger amount of money in the account.
Delegates do not have the option of modifying transactions, but may refuse their inclusion in a block and thus slow down a particular transaction. Since all delegate actions are public, any malicious behavior is visible. A large number of people want to become a delegate, so everyone who loses community confidence is replaced with the next candidate very quickly.
PROOF OF CAPACITY (PoC)
Image source: Pixabay
Cryptocurrencies: Burstcoin, SpaceMint,...
🍀Advantages:
- An ordinary hard drive can be used for mining, no special equipment is needed
- Using a hard drive is 30x more power efficient than specialized ASIC processors
- There is a higher decentralization rate compared to PoW systems
- There is no need to continuously upgrade equipment - older hard drives are also good for this principle of mining
- If a user renounces mining, he may delete data and continue to use these hard drives for other purposes
🍁Disadvantages:
- This principle of mining may be currently "favorable". The more cryptocurrencies with such system appears, the more competition between miners it will be. This could lead to a rise in the price of hard disk drives and storage of petabytes (PB), perhaps the zetabytes (ZB) of useless calculations
- It's a relatively new system with a small user share - system security is still not fully tested
- It is easy to develop malware that would use disk space for mining without the knowledge of the user
This consensus method is essentially a mining variant (PoW). PoC algorithm is a free disk space (hard disk) on your computer. It is similar to the Proof of Space concept, though it seems a bit more advanced. Specifically, PoC requires users to extract large part of the disk space to perform mining.
The main reason for this system is that the current algorithms that are dealt with, during the mining process are primitive for the average computer. The PoW system, ie "standard" mining, solves the algorithm that offers solutions to the current block. Since blocking time is fixed (eg 10 mins), ordinary computers can not solve the algorithm at the given time, they are simply too slow. At PoC, this process takes place in advance. The computer solves algorithms and solutions stored on disk. When validation needs arise, the existing, stored solutions are searched to confirm the block or transaction.
PoC may be most easily understood by this example: Imagine you have filled the disk space with the lottery numbers. Once the winning combination is pulled out, you quickly scan the disc if you have that combination. If you have, you are rewarded as a miner (miner). You can also use this combination again during the next draw - creating a new block.
In this way, ordinary computers can participate in the mining process, using the free space of the computer. If someone wants to be more competitive, more memory needs to be bought, which is relatively inexpensive compared to specialized processors / graphics cards.
BYZANTINE FAULT TOLERANCE (BFT)
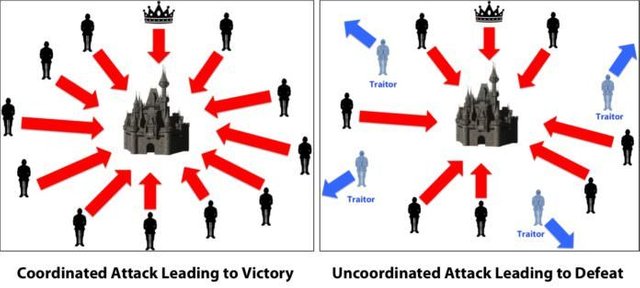
As shown on the picture above, the Byzantine generals surrounded the city with their parts of the army. Generals are differently distant and have to send messages to communicate. They have to decide unanimously whether to attack or not. If one or more generals change their decision and doesn't attack, the siege will be unsuccessful.
Cryptocurrencies: Ripple, Stellar Lumens, Hyperledger, Dispatch,...
🍀Advantages:
- It can file a large number of requests, ie transactions
- Low maintenance price
- Highly scalable system
🍁Disadvantages:
- Centralization. It requires permission to join the network
BFT refers to a known problem in distributed systems. It refers to the situation when we have a spoiled electronic component, but incomplete information about which component has been scheduled. This is a classic problem that is explained by the situation of the Byzantine Generals (hence the name). Several cryptocurrencies have developed protocols for consensus based on BFT, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
In this system, every "general" (computer) has information. When they generalize the message, they combine that message with their own information to try to solve the algorithm. The algorithm solution provides general information that helps him in deciding the question. So when making a decision about a received message, the general shares the decision with other system generals. Consensus has been reached on the basis of all decisions made by each general.
This protocol has several variants, most important of which are PBFT and FBA. PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance) is currently being used by Hyperledger Fabric.
FBA (Federated Byzantine Agreement) uses cryptocurrencies Stellar and Ripple. For FBA, each "general" (validator, node) is responsible for maintaining its own chain. Ripple is a validator pre-selected by Ripple. With Stellar, anyone can be a validator, and you decide which validator you will trust.
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)

Cryptocurrencies: IOTA, RaiBlocks (NANO), Hashgraph,...
🍀Advantages:
- High Scalability, Theoretically Current Transactions
- Low energy consumption - environmentally friendly
- Transactions are without commission
🍁Disadvantages:
- Still in development, poorly accepted due to difficult implementation
- Security has not yet been verified and tested
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a new approach to creating a cryptocurrency system. To understand DAG, imagine the tree. The wood consists of a series of pairs of large branches, which are further branched. Each stack is a node. The ramps rotate in only one direction. When a branch tears, it can never be returned on the same point of where it was torn. DAG is a graph consisting of points (nodes) that are linked in only one direction (A -> B and B -> A), and it is acyclic - it can never return to the beginning or the previous point.
Such network structure behaves completely different in contrast to the blockchain technology.
Since such a structure does not have touch points with a known blockchain, it is skeptical. It was originally presented by IOTA, which proved to be very successful because of its achievement. Namely, such a system design allows not only theoretically unlimited scalability, but also transactions without commissions. It also casts out the concept of mining. If this is the best possible system, it is hard to say. The DAG is still in development, but it has so far proved to be a very successful solution to the problems faced by blockchain.
Conclusion
I wrote about a number of different systems that achieve consensus in the cryptocureencies. There are many variations like Proof of Stake Anonymous (POA), Proof of Importance (POI), Proof of Activity (PoA) etc. It is difficult to say which of them is the best, most of them are only a few years old and only time will tell which system is best for practical application.

You got a 66.67% Upvote and Resteem from @ebargains, as well as upvotes from our curation trail followers!
If you are looking to earn a passive no hassle return on your Steem Power, delegate your SP to @ebargains by clicking on one of the ready to delegate links:
50SP | 100SP | 250SP | 500SP | 1000SP | 5000SP | Custom Amount
You will earn 80% of the voting service's earnings based on your delegated SP's prorated share of the service's SP pool daily! That is up to 38.5% APR! You can also undelegate at anytime.
We are also a very profitable curation trail leader on https://steemauto.com/. Follow @ebargains today and earn more on curation rewards!
Source
Using irrelevant tags, especially popular tags, makes it hard to find good and relevant content. Please try to use only relevant tags when posting.
steemit
steem
More information:
The Game of Tags
That's awesome information and thanks for sharing such a detailed one on different types of mining.
I am still confused between PoW and PoS although I got to know Proof of Stake seems to be advantageous over Proof of Work. May I ask you to explain more on Proof of Stake?
Thanks.
Hello,
Yes i will probably create seperate article with more detailed explanation about POS.
Thanks for the request.
I think I like POS coins better just cause you get interest for being apart of the network.
me too. having more coins doesn't mean the rich gets richer. POW also needs more powerful machine to mine more. both is about how much $ you invested. POS, coins. POW, machine.
Great post, thanks for sharing. I've smashed the upvote button for you! There need to be more articles like this, keep up the good work.
Also, if you are looking to get some tokens without investing or mining check out Crowdholding (https://www.crowdholding.com). They are a co-creation platform were you get rewarded for giving feedback to crypto startups on the platform. You can earn Crowdholding's token as well as DeepOnion, ITT, Smartcash and many other ERC-20 tokens.
I got a few questions and a few annotations to all this:
About BFT:
a) Centralization. It requires permission to join the network
What do you mean by that? Most BFT protocols, especially PBFT are not centralized at all. Especially, to avoid single point of failures.
b) Scalability.
I wouldn't exactly name BFT protocols highly scalable since outside of the blockchain world they are rarely used, even considering their great advantages considering byzantine failures.
I've written a few articles about scalability of BFT systems and, if they're not built hierarchically, they don't scale well at all.
Might scale better than many of the other approaches named here though.
About the others:
I had always thought all blockchains use some kind of byzantine agreement. If not for the verification of new blocks, but for the verification of transactions. Is that wrong?
I mean, I understand how they verify the new blocks with PoS and PoW but do they use that to verify the transactions as well?
(For example, if one server decides to send not existing transactions to enrich himself)
Hi @arhitekt,
Thank you for taking out time to write such informative post.
Can we say PoS is for individuals like normal people who mine and PoW is for some people who are designated ones like Witnesses in case of Steemit?
And yes, Delegated PoS resembles the Steemit mining and activities going on Steemit.
PoC seems to be for common man like me, but it has security issues as you mentioned and may not be trusted.
Although the blockchain jargon are confusing but I am sure as we explore and use these mining things we will get used with these.
Appreciate your time on exploring these things and writing a neat blog with all the details.
Following you now.
You got a 56.82% upvote from @brupvoter courtesy of @arhitekt!
and what about hashgraph?
To listen to the audio version of this article click on the play image.

Brought to you by @tts. If you find it useful please consider upvote this reply.