COMMUNICABLE DISEASES. FIRST PART
Hello dear friends of steemit, today I am going to give you a brief introduction to communicable diseases, how they are transmitted and how they are prevented, in my next post I will be talking about the types of communicable diseases that exist and we will talk about the most relevant ones.

Source
Transmissible diseases are those caused by the entry, development and multiplication of an infectious agent in a person's body. Its fundamental characteristic is that it is transmitted from person to person, either by direct or indirect contact.
The mortality of these conditions has decreased as a consequence of early diagnosis and the application of highly effective drugs.
ETIOLOGY OF COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
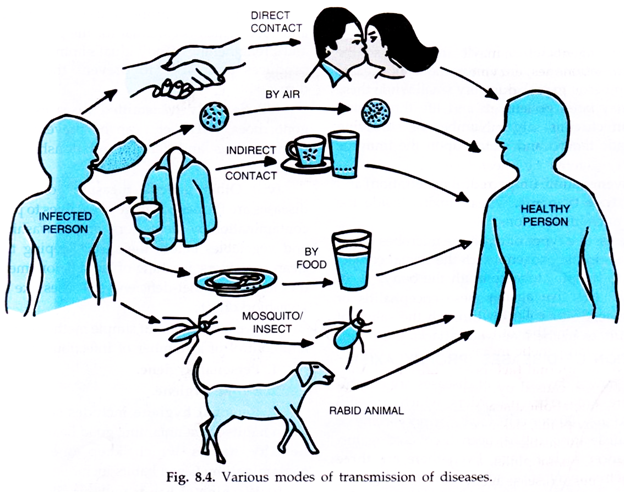
Infectious agents are living organisms that can be included in one of the following groups: protozoa, bacteria, viruses, spirochetes, fungi and helminths. These diseases are contracted through different mechanisms:
Direct transmission
It is the direct transfer of the agent to a receptive gateway. The transmission occurs when kissing, touching, having sex, or droplets that, containing the agent, reach the potential guest as a result of coughing, sneezing or speaking of other people. In the case of mycosis (fungi), the contagion takes place through the soil or by stepping on decomposing plant material.
Indirect transmission
It occurs when an agent reaches the host through an intermediary vehicle; The most common are food, water, toys and clothes. There are also biological intermediaries; some act as mechanical transport, as in the case of flies, while in others, as with the mosquito, the agent undergoes a series of transformations within it before entering the human body.
PRECAUTIONARY MEASURES
Preventive measures can be collective or individual; the former are the responsibility of the health agencies and are related to the risk of the population and the resources it has against a certain disease; the latter depend fundamentally on the individual and are related to factors such as hygiene and nutrition.
Measures against sources of infection
In diseases such as tuberculosis, smallpox, scarlet fever, among others, in which man is the main reservoir, isolation during the period of transmissibility is the main preventive measure. In those whose source of contagion is hydric, it corresponds to the adequate treatment of water and everything that may be contaminated by it, especially food.
When the reservoir is an animal, veterinary surveillance corresponds. Many of these diseases are treatable, but it is usually more economically and epidemiologically more effective, the slaughter of sick animals.
Measures against the transmission routes
Each communicable disease has its modes of propagation. In the case of indirect transmission through water, which is both a reservoir and an infectious agent route, it is essential, as we have already said, to treat the water that is used for drinking, the sanitary control of irrigation water and water. the food in all its phases.
Measures against the susceptible host
We have a set of body defense mechanisms against the invasion or multiplication of infectious agents. In the first instance there is a natural resistance in each individual, generally linked to its constitution and favored by its nutritional status and personal hygiene.
In the second instance there is a state of resistance associated with the presence of antibodies that, via the placenta, pass from the mother to the fetus and serve as stimuli for the creation of new antibodies. Artificially protective specific antibodies can also be inoculated, this immunity is short-lived and is called passive immunity.
Active immunity that lasts for months or years can be acquired naturally as a consequence of an infection, as in the case of measles, or artificially, by inoculation of fractions or products of an infectious agent or by the same agent killed or attenuated in its pathogenic capacity . These products are called vaccines, and all of them stimulate the formation of antibodies against a certain disease.
Source
References:
Curso de Orientación Familiar. Medicina y Salud. Ediciones Océano, S.A
For more information, visit the following pages:
http://www.open.edu/openlearncreate/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=84&printable=1
http://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/communicable-diseases
http://www.open.edu/openlearncreate/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=85&printable=1
@angelinaa, Very informative and nice article on communicable diseases.
Thank you very much @drvnpatel