the atmosphere, weather and climate
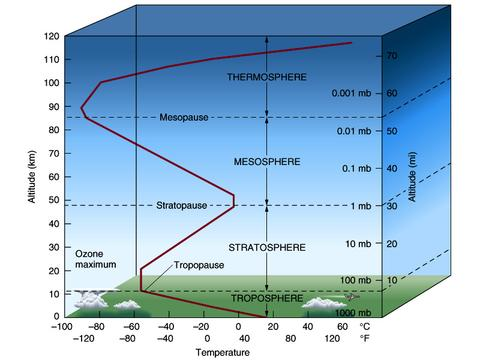
Hello steemians today come to document you about the atmosphere, weather and climate with an analyzed research, the atomosphere (drawing from above) is the gaseous layer that surrounds the earth: an air layer of up to 1,000 km thick; it changes composition and temperature with altitude.
It is essential for life, since it protects the planet from harmful radiation from the sun and prevents excessive warming of the earth's surface, where the air needed for breathing and in its lower layers, especially in the troposphere (the one closest to the surface), occurs most of the phenomena (winds, clouds, rain, etc.) that determine weather and climate.
From the temperature point of view, it is divided into four layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. It can also be divided, according to its chemical composition, into three layers: homosexual, heterosphere and exosphere. Temperature deviations on the Earth's surface cause the movement of atmospheric air masses, which circulate around the planet following regular patterns.
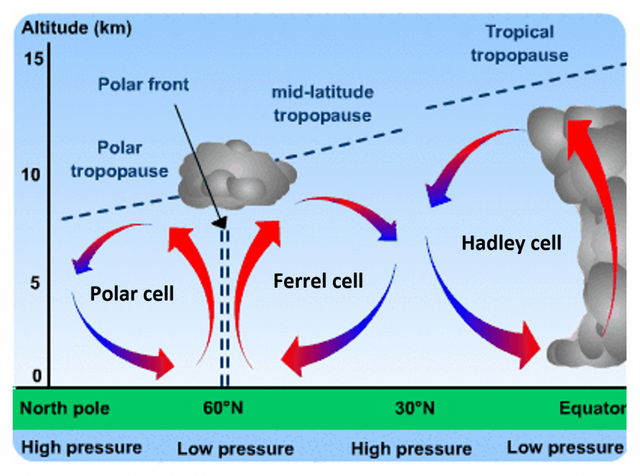
General atmospheric circulation.
there are large bands of low pressure (where the hot air rises) and high pressure (where the cold air descends) on the earth, alternating from the equator to the poles. The movement of air between them is the general atmospheric circulation.
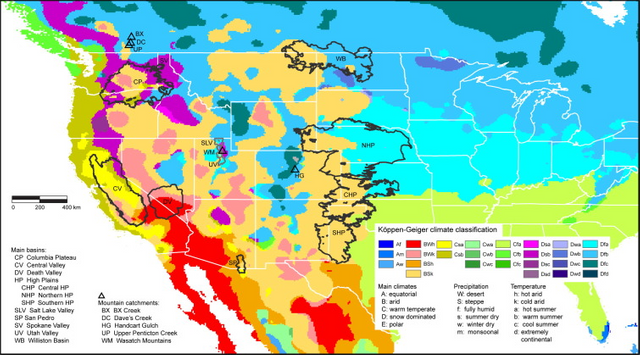
The surface of the earth is divided into large areas with a similar climate, oriented according to the parallels, which follow one another from the equator to the poles (upper map). In each climatic region the annual variation of temperatures and forecasts has certain characteristics.
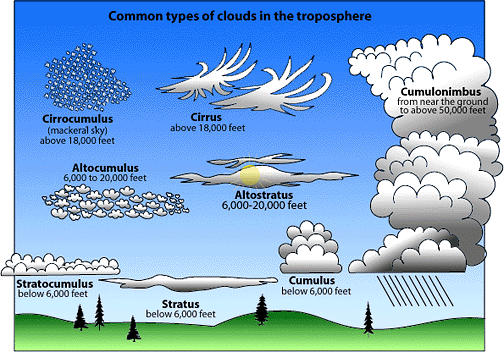
Clouds, responsible for many aspects of atmospheric weather, are classified into eight different types (above) according to the altitude at which they are formed, and the shape and color they present. hya above all horizontal, as strata, or vertically developed, such as cumulonimbus
sources of information.
