Pathological Aspect Of Extinction #3; Factors That Influence The Rate Of Extinction ( Part 1)
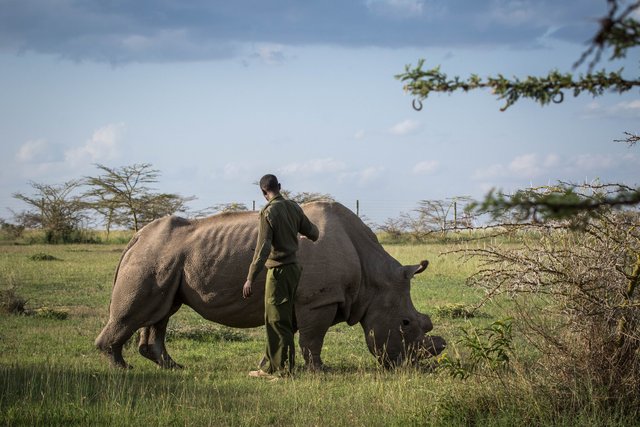

Hi everyone,
In the previous article, we've learned quite a bit about the background extinction. It is important for us to understand that extinction is not necessarily abnormal. It's completely a normal biological/ecological process and every single living things on earth extinct at a different rate. When they disappear, their roles would be taken over by a new emerging species, so the ecosystem is not or only slightly affected by this phenomenon. For those who missed both of the articles I released a week ago, you can click the links below to find out.
Initially, I thought this series could be divided into four parts of articles, but it turns out, I've underestimated the amount of information which can be found in this particular discipline. Hence, I'll be continuing this series without actually stating the number of parts required for it to finish. For the next few articles, we would explore some of the reasons why the current extinction rate exceeds the background extinction. The factors can be divided into six:
- Loss of habitat
- Pollution
- Introduced species
- Overharvesting
- Secondary extinction
- Global changes
In this article, we would give our attention to just one of the factors which can affect the rate of extinction; habitat loss. The rest of the factors would be explained in the subsequent article. Let's get on it.
Loss of Habitat
Habitat loss is one of the most critical factors which could affect the current rate of extinction. I think it is clear and pretty much understood by everyone that the destruction of coral reef and deforestation would eliminate any species which can be found in that particular area. This phenomenon is termed as the local extinction. Even though the difference between local and global extinction is clear-cut, the word "extinction" is usually used to indicate a total obliteration of species from the face of the earth (global extinction). Local extinction has been called as extirpation for the sake of differentiating both of this phenomenon.
To make it easier, I've divided the discussion regarding habitat loss into three groups:
- Terrestrial species
- Marine's species
- Freshwater species
Terrestrial Species
The area which has been documented with a high rate of local extinction is known to hold an abundance and variety of species which are specific to that particular location. This is called as endemism. Endemic species were usually concentrated in a particular area. They are typically found on a remote island, living in a perfectly balanced ecosystem until human discovered that particular island. Yes, I'm talking about Hawaiian island, and if you have read the part 2 of this series, you would know what I meant.
- A study conducted in the past has proved that the majority (almost 90%) of species which lives on the Hawaiian island are endemic to that location (it doesn't exist anywhere else).
- Nearly 70% of the total flowering plant's population in South Africa are endemic.
- There are as much as three-quarters of endemic species living in Australia.
If we considered that every single species has the same risk of extinction, then the probability of a particular species to extinct would be proportional to the number of that species living in a specific region. This assumption only works if the species which are included in the equation are in fact, endemic to that particular region. In the past, Hawaiian island and Great Britain possessed the same number of terrestrial bird species, but as what has been illustrated in the previous article, Hawaii loses more than 100 species of terrestrial birds compared to the Great Britain which only suffers a few losses as a result of human's activities.
Do you want to guess why is it so? Most of the species which live on Hawaiian island were endemic while in Great Britain, only one of all the terrestrial bird species was endemic. It proves that the rate of extinction depends on the concentration of the endemic species living in that particular location. Unless the island or region is free from all of the human's activities, then, the area which has the highest concentration of endemic species would lose the most.

The aforementioned theories can only be valid if the risk of extinction of every single species on earth is the same. What if their rate of extinction is different? What kind of variable which we would use to predict which species would lose the most? Well, if the risk of extinction between all species is different, the best predictor of extinction would be the size of geographic distribution (range). Any species which are distributed within a small range of geographic location were vulnerable to be annihilated.
There are a few characteristics of terrestrial life distribution:
- The range size of the majority of the terrestrial species is small.
- This small range size terrestrial species usually have low population densities (it is difficult to find them even if you are within their territory).
- This small range size terrestrial species are typically concentrated, geographically.
Some of the areas which are inhabited by small range group of endemic terrestrial creatures have been marked as the terrestrial hotspots. There are about 25 hotspots that have been discovered in the 1990s by researchers which concurred with human's activities. The number of different species resides in this particular area have a high degree of concentration which can be summarised as follow:
- There are 133,000 species out of 300,000 species of flowering plants.
- There are 2,800 species out of 10,000 species of birds.
- There are 1,300 species out of 5,000 species of mammals.
- There are 3,000 species out of 8,000 species of reptiles.
- There are 2,600 species out of 5000 species of amphibians.
The effect of human's activity on all of these 25 terrestrial hotspots is so severe that less than 1/8 of them survived til now. The majority of this terrestrial hotspots are forest which is affected by deforestation for agriculture and logging. Less than 2/5 out of the number of terrestrial hotspots which survived now are currently under protection. Since a lot of activities have caused some of the species to lose their habitat, they migrated to the respective terrestrial hotspot (whichever is near) and these areas become concentrated with a lot of threatened or recently extinct species. If the area is meant to be destroyed by humans, then we can expect the number of species which would disappear from the exosystem will reach up to hundred thousands species.
Marine's Species

People know that the oceans are vast. There are so many things which remain as mysteries, waiting to be discovered which include an abundance of expected yet-to-be-discovered species. Out of 1,500,000 species which has been documented by scientists, only 210,000 of those were marine animals. It is relatively small figures compared to the fact that two-thirds of the Earth are covered with oceans so the actual numbers might be higher than what we've expected. In the early of 21st century, a strenuous effort taken by various international programs to record the marine's life species has only found 13,000 new species in the matter of decades. Ocean exploration is a difficult task thus the amount of time required to identify at least more the actual half of marine's life would take a few decades more or even a millennium.
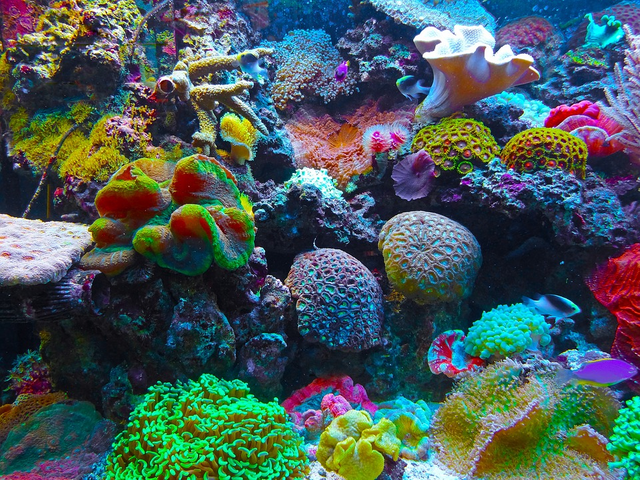
Coral reefs which hold one-third of the discovered marine's life is the rainforest of the sea. There are about 100,000 species which has been identified, but that only accounts for 0.2% of the total area of the sea. The fact that at least one-third of the discovered marine's species can be found in this form of habitat, it signal importance of conserving it to avoid an abnormal background rate of extinction of other species of marine lives. After a careful, species mapping effort on a global scale, it was found that most of the marine's species were concentrated in the ocean located around Indonesian islands and Philippines. Apart from that area, Caribbean also has a higher form of marine's biodiversity which represent one of the few marine's hotspots.
All of the regions which have the highest concentration of marine's biodiversity usually have the least number of endemic species. There are a few places which can be thought as the central area for endemic life form in the seas which are:
- The Gulf of Guinea
- Sunda islands
- Mascarene islands
- Southern of Japan
- Philippines
Most of the coral reefs can be found within the area of developing countries except for the Great Barrier Reef in Australia. Most of them are threatened with extinction due to abnormal fishing activities by some desperate people who tried to cope with the declining rate of fish catches. This phenomenon is attributable to the increase in human population and poverty which drives them to use some unusual methods to increase their daily income. Throwing dynamite into an area filled with potential marine's catches is one form of abuse imposed on the marine's life; some of them even resorted to poison use. This could potentially threaten the integrity of the coral reefs which caused them to decline in number, consequently, make the number of marine's life to reduce as well, hence the low catch rate.
There are a few other reasons which cause the coral reefs to decline:
- Global warming
- Coastal development
- Pollution
The most affected area which imposed a significant amount of damage on the coral reefs would be the areas which have the highest rate of deforestation activities. This particular activity is not only disrupting the habitat of a specific terrestrial species, but it also causes the soils to erode, and be washed off by the rains onto the coral reefs. The extent of destruction caused by human's activities on terrestrial creatures indirectly affecting the marine's extinction rate by destroying its version of the rainforest; the coral reef.
Bottom trawling or net dragging along the sea floor is one of the most critical factors which imposed a severe risk of marine's life extinction. This method of catching fish was developed to optimise yield but at the same time, damage the physical integrity of the sea floor which has been the habitat of various species of fishes. I think not many people knew that the damage which has been caused to the sea floor is much more significant than the damage imposed to the tropical forest caused by deforestation. The effect on the marine's ecosystem is rarely seen which lead to underestimation.
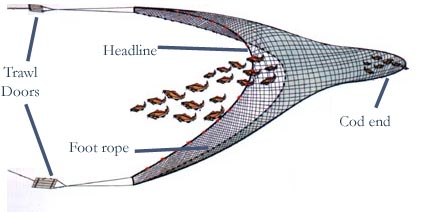
Each year, the disruption imposed by trawling on the global sea floor can be up to 15 million square kilometres. Even though the area only covered 4% of the world's total, it's still caused significant damage and instability to the local ecosystem. It is because the majority of the oceanic area was composed of deep water regions which are poor in nutrients. We can say that the deepwater area of the ocean is the equivalent of a desert so most of the marine's species can be found in the continental-shelf which is the area of nutrient-rich water covering almost 30 million square kilometres. Some species which are affected by trawling include:
- Brachiopods
- Molluscs
- Sea urchins
- Corals
- Polychaete Worms
Freshwater's Species

Damming and channelisation have been two important reasons why some of the freshwater's species are threatened with extinction. There are two major classes of freshwater species in the freshwater ecosystem:
- Flowing (rivers)
- Static (ponds)
Unlike terrestrial and marine's species, there is a lack of information regarding the distribution of freshwater species in a specific area. The only things that we can say for sure are, the pattern of distribution for most of the threatened species are concentrated to a particular location. The majority of freshwater's fishes can be found along the tributaries of Amazon river and a few other Tropical rivers. There are a large number of endemic species of freshwater fishes which reside in East Africa.
Any human's activities which attempt to modify the flow of rivers can potentially destroy the natural habitat for a specific species of freshwater fishes. As I mentioned above, damming and channelisation can be quite harmful to the freshwater ecosystem.
Channelisation is a river engineering method that deepens or widen rivers to increase their capacity for the volume of flow at specific sections of the river.
A study which has been conducted in the early 21st century has revealed that most of the world's large river was modified to assume the pathway which could be beneficial for human's activities, i.e. agriculture. Whatever modifications made by using whichever method, we can agree that all of this attempt to reap off potential benefit will cost the life of the freshwater's resident.
References and further reading materials
- Callicott, J. Baird. 2006. “Conservation Values and Ethics.” Pp. 111-35 in Principles of Conservation Biology, 3rded., edited by M. J. Groom, G. K. Meffe, and C. R. Carroll. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer.
- Stuart L. Pimm. Encyclopaedia Britannica. Conservation. Retrieved March 27, 2018, from https://www.britannica.com/science/conservation-ecology
- Alberta Water Portal Society. Flood Mitigation: Channelization. Retrieved March 27, 2018, from https://albertawater.com/flood-mitigation/river-bank-protection
- Wikipedia. Extinction. Retrieved March 20, 2018, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extinction










Congratulations! Your post has been selected as a daily Steemit truffle! It is listed on rank 21 of all contributions awarded today. You can find the TOP DAILY TRUFFLE PICKS HERE.
I upvoted your contribution because to my mind your post is at least 14 SBD worth and should receive 85 votes. It's now up to the lovely Steemit community to make this come true.
I am
TrufflePig, an Artificial Intelligence Bot that helps minnows and content curators using Machine Learning. If you are curious how I select content, you can find an explanation here!Have a nice day and sincerely yours,
TrufflePigbeautiful i like it.....
I'm not sure I understand which part is beautiful. Care to elaborate?
I love animals , please people save the animals 😟😇💙
I'm sure a lot of them are trying.
When we tell our kids about some of these animals, it would sound like a scifi movie gone wrong.
Maybe the future "Jurassic Park" will consists of some of the animals which are living today.
Cool, I think I have to read your first two articles to understand it better.
Thanks for reading it. Glad you like it.
I recently learned that extinction was a normal aspect of life. This is an excellent article that goes very much in depth on the subject. Thanks for sharing!
Yes, you are right, extinction is perfectly normal, it just how quick its progress that would determine is it pathological or is it natural.
Interesting..The same way we humans are entitled to extinct one day..Isn't it?
Well, I'm not sure but it is a possibility.
This post has been upvoted and picked by Daily Picked #17! Thank you for the cool and quality content. Keep going!
Don’t forget I’m not a robot. I explore, read, upvote and share manually :)
Great post, @chloroform! I'm glad to see that you are posting about conservation biology; it's such an important topic! Ecological hotspots are really important, and it sucks that we are so bad at taking care of them.
Anyway, I kept thinking about how you should mention how habitat fragmentation ties in to a lot of this, but I guess you have it planned for another post?
Best regards from @valth
I wasn't planning to explain about habitat fragmentation at first, but now you make curious. Thank you for the suggestion.
Oh, you're welcome. Habitat fragmentation is often almost as damaging to many species as the directly lost habitat destruction. Here in Norway we have seen that both large carnivores such as bears and wolves, as well as reindeer have been having population declines as a direct result of habitat fragmentation.