PLASMA: the fourth state of matter
Matter in its simplest form refers to any substance which has mass and occupies space. All matter is made up of atoms sometimes bonded together closely or scattered widely.
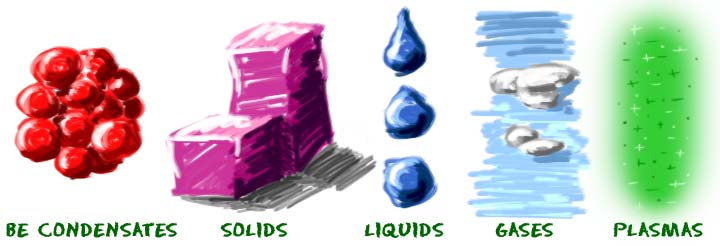
Image source
States of matter are generally described on the basis of qualities that can be seen or felt.solids are often hard, liquids fill container and gas surrounds us in the air. Each of these states is also known as a phase .
how does matter change from one state to another
Elements and compound can change from one state to another when certain physical conditions are changed, For example, when the
temperature of a system is increased, the matter in the system becomes more excited and active. If enough energy is pushed into a system, a phase change may occur as the matter moves to a more active state.
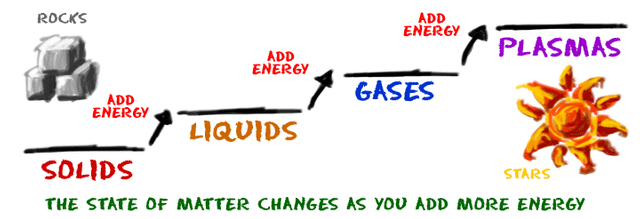
Image source
Let’s say you have a glass of water (H2O). When the temperature of the water goes up, the molecules get more excited and bounce around a lot more. If you give a liquid water molecule enough energy, it escapes the liquid phase and becomes a gas . The extra energy allows the molecules to change states.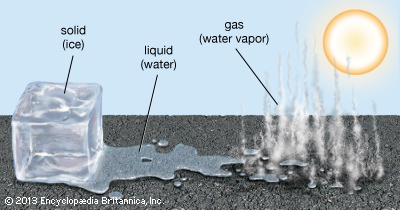
Image source
Have you ever noticed that you can smell a fish frying from a distance after it starts to heat up? As the energy of the molecules inside the fish heat up, they escape as a gas. You are able to smell the
volatile compounds that are mixed in the air around you.
Phases of matter includes;
Solids
solids as a phase refers to substances that has a definite shape and volume because the molecules that make up the solid are packed closely together and move slowly. Solids are often crystalline; examples of crystalline solids include table salt, sugar, diamonds, and many other minerals. Solids are sometimes formed when liquids or gasses are cooled; ice is an example of a cooled liquid which has become solid.
Other examples of solids include wood, metal, and rock at room temperature.
Liquids
A liquid has a definite volume but takes the shape of its container. Examples of liquids include water and oil. Gasses may liquefy when they cool, as is the case with water vapor. This occurs as the molecules in the gas slow down and lose energy. Solids may liquefy when they heat up; molten lava is an example of solid rock which has liquefied as a result of intense heat.
Gases
A gas has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. Some gasses can be seen and felt, while others are intangible for human beings. Examples of gases are air, oxygen, and helium. Earth's atmosphere is made up of gases including nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Plasma
Plasma as the fourth state of matter has neither a definite volume nor a definite shape. Plasma often is seen in ionized gases, but it is distinct from a gas because it possesses unique properties. Plasma is a state of matter where the gas phase is energized until atomic electrons are no longer associated with any particular atomic nucleus . Plasmas are made up of positively charged ions and unbound electrons. Plasma may be produced by either heating a gas until it ionized or by subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field.The plasma may be formed by heating and ionizing a gas. Examples of plasma include stars, lightning, fluorescent lights and neon signs .
phase transitions
Matter undergoes phase changes or phase transitions from one state of matter to another.
form from sublimation of solids, vaporization of liquids, and recombination of plasma.
Melting
solid → liquid
Example: Melting of an ice cube into water.
Freezing
liquid → solid
Examples: Freezing sweetened cream into ice cream.
Vaporization
liquid → gas
Example: Evaporation of alcohol into its vapor.
Condensation
gas → liquid
Example: Condensation of water vapor into dew drops.
Deposition
gas → solid
Example: Deposition of silver vapor in a vacuum chamber onto a surface to make a solid layer for a mirror.
Sublimation
solid → gas
Example: Sublimation of dry ice (solid carbon dioxide) into carbon dioxide gas. Another example is when ice directly transitions into water vapor on a cold, windy winter day.
Ionization
gas → plasma
Example: Ionization of particles in the upper atmosphere to form the aurora. Ionization may be observed inside a plasma ball novelty toy.
Recombination
plasma → gas
Example: Turning off power to a neon light, allowing the ionized particles to return to the gas.
uses of plasma
Plasma is used in television, neon signs and
fluorescent lights . Stars, lightning, the aurora, and some flames consist of plasma.
Where Can I Find Plasma?
You probably encounter plasma more often than you think. More exotic sources of plasma include particles in nuclear fusion reactors and weapons, but everyday sources include the Sun, lightning, fire, and neon signs. Other examples of plasma include static electricity, plasma balls.
Thanks for stopping by