Wind and atmospheric circulation
As we all know, wind is as a result of difference in pressure from one region to another on the earth surface. Air moves from area of high to low pressure, and when it does so, it is called wind, we can also say wind is air in motion. It is also called airmass. The movement of winds on the earth surface is called atmospheric circulation.
what is responsible for atmospheric circulation?
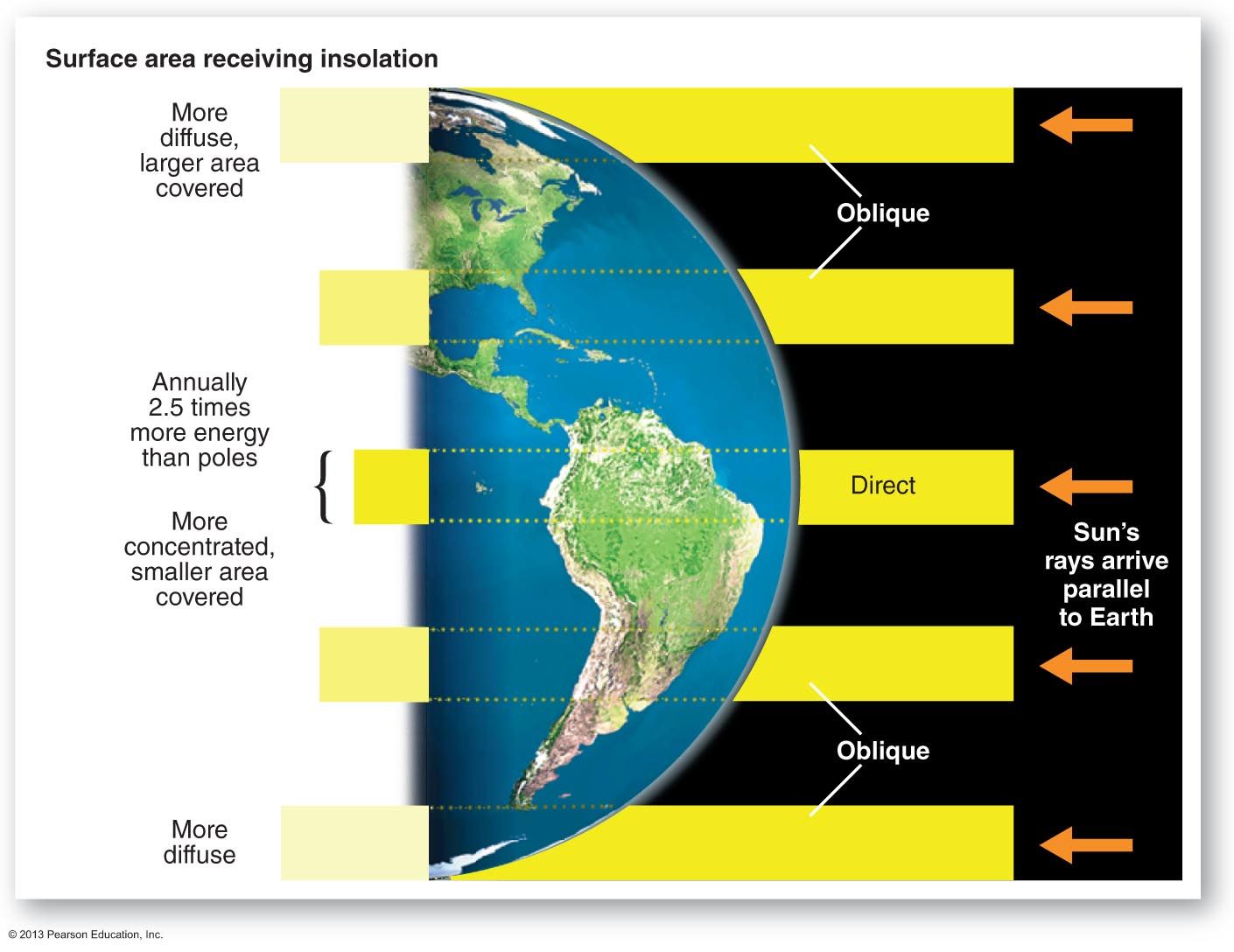
One of the main causes of winds is the difference in the heating of the earth surface. When an area is heated, the air expands and rises, low pressure is created there, so air rushes from areas of higher pressure around to this area of low pressure to take the place of risen air.
Credit
The earth's rotation also causes winds, for it generates centrifugal force which sets wind in motion.
The direction and speed of winds are determined by three vital factors which are, pressure gradient, earth's rotation and surface friction.
Pressure gradient is the difference in pressure between any two places. The higher this gradient, the stronger the wind, the same way as a vehicle rolls faster down a steeper slope than down a more gentle slope.
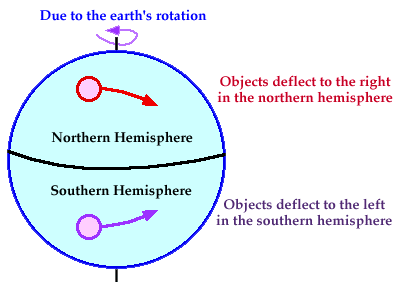
The earth’s rotation also generates another force called the Coriolis force. This force deflects the winds to the right in the northern hemisphere, and to the right in the south.
Credit
The surface of the earth, mountains and trees which lie across the wind path create surface friction which tends to retard the speed of the friction.
Reference
http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/fw/crls.rxml
[Wikipedia](https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atmospheric circulation)
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/geophysical/chapter/global-atmospheric-circulations/