BIOLUMINESCENCE: THE LINK BETWEEN LIGHT AND LIFE

INTRODUCTION
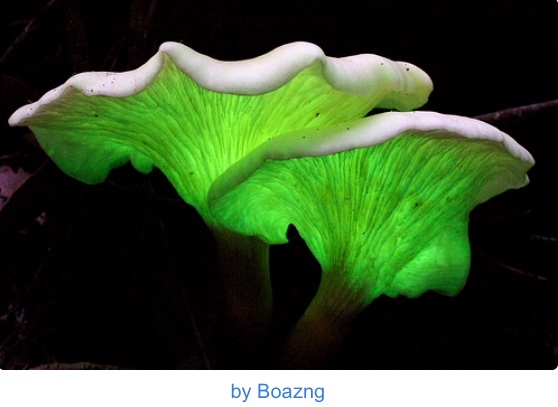
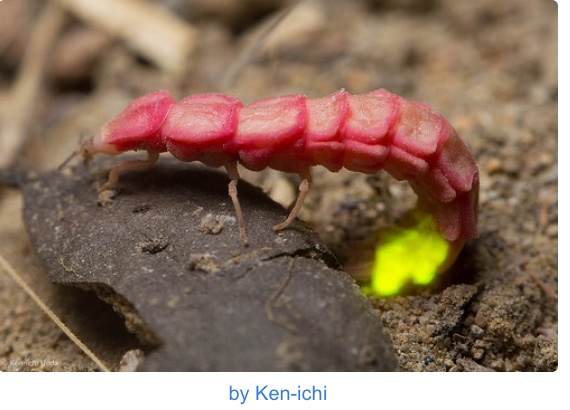
Ever gone on a walk and seen a collection of fireflies and gotten instantly amazed at how brightly and colorfully they glow ? Well, I bet we all have. The phenomenon of this glowing is termed “Bioluminescence” and it is almost entirely a biochemical process. From fireflies to glow worms to click beetles and practically, most marine animals, bioluminescence has been a common characteristic.


Humans actually view bioluminescence as a way animals get to show off their lights but animals only light up as a result of responses to attacks or on a quest to attract a mate. It’s also a common misconception that bioluminescence is actually common on land among fireflies but in factuality, it is extremely common in the deep sea since it is so vast and thus the need for bioluminescence as a common form of communication.

Bioluminescence is the emission of light from an organism (living) to aid in its survival or multiplication. It is a biochemical process that occurs through a chemical reaction which produces light within the body of an organism. The main factor responsible for Bioluminescence in organisms is “Luciferin”. Luciferin is present as different types in different organisms. Interestingly, bioluminescent organisms possess in addition to Luciferin, an enzyme known as Luciferase which speeds up the whole chemical reaction process.


Organisms can fully control when they light up by regulating certain chemistry and brain processes depending on their present needs, food or a mate. Some organisms even contain the Luciferin in bond with oxygen (this is called a photoprotein) so they can instantly light up when a required cofactor ion such as magnesium is present. They independently choose the colour and intensity of the lights they emit.
How widely is Bioluminescence distributed ?


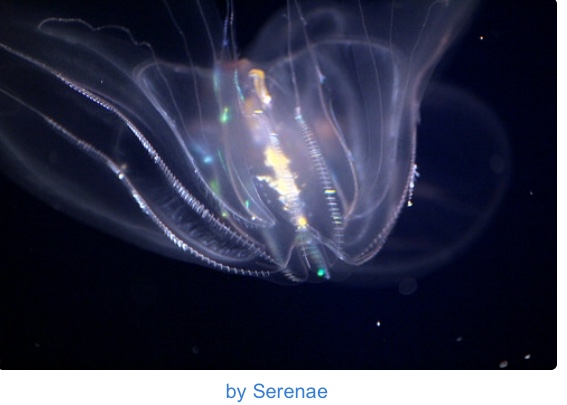
Bioluminescence is found basically at every point on the biosphere but only among mammals and plants. It occurs in random distribution among genera, in some cases, in some species within a specific genus and not other species in the same genus for reasons quite not so evident. About 17 phyla and 700 genera comprise species with luminous properties. Bioluminescence has been found among many fish, cephalopods, annelids, jelly fish, ostracod, just to make a few marine animals. The glow worms, fireflies, click beetles, some luminescent fungi are mainly predominant on land. Many luminous organisms however remain to be discovered.

In terms of anatomical distribution, Bioluminescence is mostly found in a key organ known as the photophore (the light producing organ) which is seen in luminous fish and very clearly in cephalopods. Reaction components important for Bioluminescence can also be found in the stomach, liver and organs of secretion of certain organisms.

Geographic distribution shows that bioluminescence is found in organisms world wide. From oceans, particularly this coral reefs and bays to the Bioluminescent bay found in Puerto Rico to the temperate regions in America, Asia and China. Bioluminescence is ubiquitous.
Biochemistry of Bioluminescence
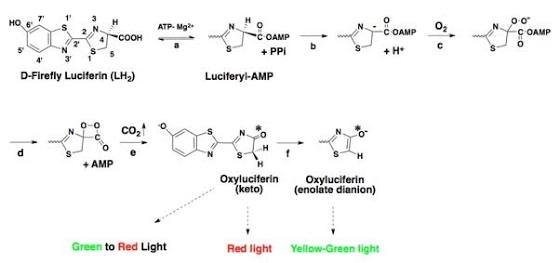
Credit:source
Bioluminescence is as a result of the oxidation by oxygen of Luciferin by an enzyme known as Luciferase. This reaction is heavily dependent on cofactors such as magnesium, calcium or ATP depending on the organism involved. Fireflies are known to use magnesium and ATP while the photoprotein aequorin requires calcium ions which is used by the Aequorea victoria.
Addition of a cofactor such as calcium causes a quick catalysis which produces a brief flash in the Aequorea victoria but a prolonged glow is produced in fireflies by the Luciferase enzyme component. In a second step which is much slower, Luciferin is regenerated from oxyluciferin which recombined with aequorin to produce a flash.
A particular Luciferin is coelenterazine found in most vertebrates and responsible for their bioluminescence. Not all organisms can synthesize this Luciferin and some need to obtain it through diet.
Are there any specific colors of bioluminescence ?

It’s no secret that the colours of light are determined primarily by their wavelengths. Light hits our eyes and is translated into different colors depending on wavelength. The electromagnetic spectrum is made up of the visible and non-visible light spectrum. Humans can only see light in the visible region. In fact we can only see all the lights in the visible spectrum when they travel through the air above the land. But light takes a different traveling approach under water majorly because longer wavelengths can’t travel far in this environment. It is therefore of little wonder that most of the bioluminescence we see under water is in the form of blue-green light. Blue and green lights have shorter wavelengths and thus can travel easily in deep water and can also be seen. Lights of longer wavelengths such as the red light doesn’t reach the depths of the sea that’s why many deep sea animals are red and practically invisible although some organisms have evolved and developed means to emit and also detect red light.
Reasons for bioluminescence (why animals light up)
- Feeding:Some animals use light to lure their prey or in some cases, light up their surroundings to see their prey better. A notable example is the Stauroteuthis octopus which uses its bioluminescent beak to attract prey. The cookie-cutter shark is also known for using bioluminescence to fool its prey including whales and having a bite out of them.
- Attracting mates: Ever wondered why fireflies light up ? I bet you thought it was just for fun. Well like I earlier pointed out, animals don’t light up for fun. They do so for survival and propagation. The firefly is an example of an organism which lights up for propagation. The male and female fireflies both light up for the purpose of mating. There are two systems of bioluminescence in the firefly which is dependent on species. In one species, the female firefly emits light from its abdomen to attract males while in the other species, the flying males emit light signals to which females respond. The click beetles also emit light but from two body parts; from the abdomen when flying (orange light) and from the thorax when disturbed or on the ground (green). The former is a sexual attraction factor while the latter is in purpose of defense.

Credit:Wikipedia
- Camouflage: when we hear of the chameleon, we pretty much of the word “camouflage” or maybe it is when we hear of the Nigerian army but that’s a story for another day. Deep sea animals are known to use bioluminescence for the means of camouflage through an exceptional process known as counterillumination. The organism matches its environmental lights as viewed from underneath. Squids and certain fish possess this property.
- Defence: Cephalopods and certain squids possess a property where they use bioluminescent chemicals just as squids are known to use ink. This chemical mixture is used to distract, expel and repel predators while escaping to safety. Some organisms twitch and flash as a means to distract predators while they flee.

- Warning: some organisms use bioluminescence to provide warnings that they are not palatable. This is known as Aposematism. Many firefly larvae and millipedes use this defence mechanism. Certain worms, jelly fish and Cnidarians also use this
- Communication: Some organisms use bioluminescence as a means of communication. Pyrosomes possess luminescent organs which turn on and off when stimulated by light causing rhythmic flashing. The Quantula striata is another example of an organism that uses bioluminescence for communication.
- Mimicry: The anglerfish and the dragonfish aggressively mimic other species just to attract prey. The esca which is an appendage on their heads contains bacteria with bioluminescent properties that produce the glow that the fish can exert control over. Female Photuris fireflies can mimic the pattern of the photinus, another firefly, just for the purpose of attracting its male as prey.
Bioluminescence and it’s usefulness in Biotechnology
- Biology and Medicine: Bioluminescence is used in multiple areas of research. Luciferase based systems are used in molecular biology as detector genes as they each exhibit a different colour on fluorescence as well as for biochemical research. Bioluminescence is used in cancer treatment too as it can be harnessed to destroy cancer cells. Optogenetics is also a process that involves bioluminescence where light is used to control cells in living tissues especially neurons which have been modified genetically to show ion channels sensitive to light.
- Light Production: the light producing properties of organisms can be harnessed through genetic engineering and used possibly in the future to reduce the need for steeet lighting and also for purposes of decoration if the production of bright and sustainable light becomes a possibility.
- There is also ideas and interesting applications that exist in which bioluminescence can be applied in the creation of luminous Christmas trees and walkways not excluding luminescent champagne and beer. Read more here
- The use of light sticks in airports to guide airplanes as well as in concerts is an application of the phenomenon of luminescence. Read more here
What are the questions that remain regarding bioluminescence ?
- how is bioluminescence beneficial to earthworms if they still get eaten anyway ?
- The firefly light up is solely for sexual interaction but why is there a synchrony of the firefly Christmas tree ?
- What are the dietary sources of the Luciferins I earlier mentioned ?
- What exact molecular mechanisms control light flashing ?
REFERENCES
- What is Bioluminescence ?
- How widely is Bioluminescence distributed ?
- Biochemistry of Bioluminescence
- Are there any specific colors of bioluminescence ?
- Reasons for bioluminescence (why animals light up)
- Feeding
- Attracting mates
- Camouflage
- Defence
- Warning
- Communication
- Mimicry
- Bioluminescence and it’s usefulness in Biotechnology
IMAGE SOURCE
All images used here, are free images from Photopin via wikicommon and flickr
The names of the original owners of the photos are also recognized as seen underneath each image.
THANKS FOR READING !!!!!!!

Wow! This is an extremely detailed post... both your points and the picture you made use of are dope. Nice one dear
Thank you
Very interesting read. Really amazing post. Well done.