Are the inhibitors the most effective way to control corrosion?
Corrosion is understood as the interaction of a metal with the environment that surrounds it, producing the consequent deterioration in its physical and chemical properties.
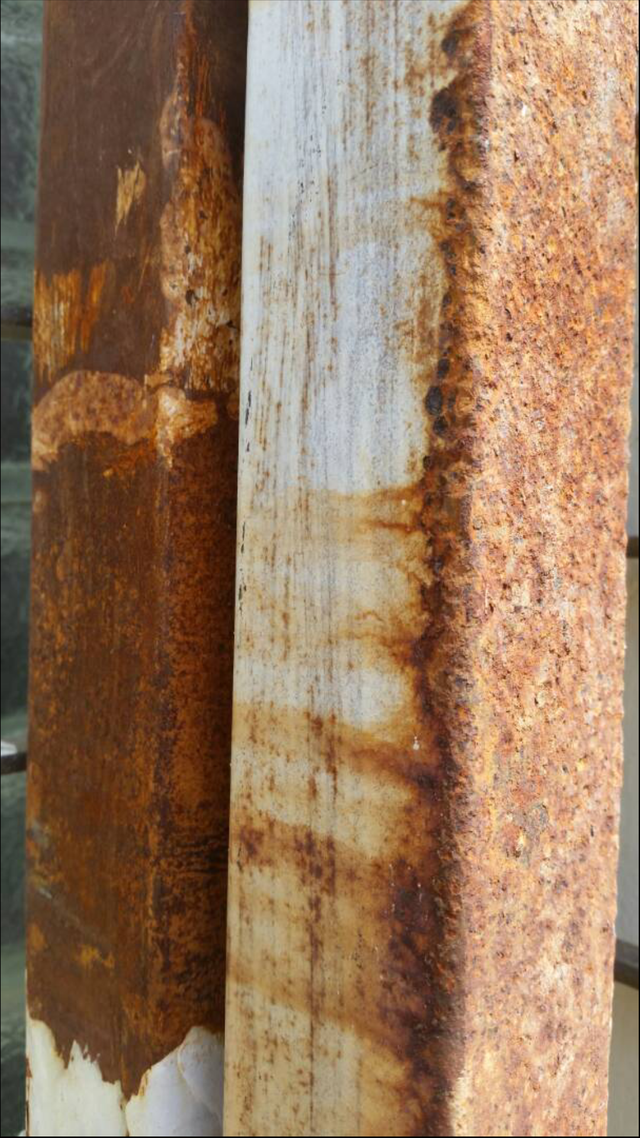

The fundamental characteristic of this phenomenon is that it only occurs in the presence of an electrolyte, causing fully identified regions, called anodic and cathodic: an oxidation reaction is an anodic reaction, in which electrons are released to other cathodic regions. In the anodic region the dissolution of the metal (corrosion) will occur and, consequently in the cathodic region, the immunity of the metal. The speed at which a material corrodes is slow and continuous, all depending on the environment where it is, as time goes by creating a thin layer of material on the surface, which are initially formed as spots until they reach imperfections appear on the surface of the metal. The environment then is an important factor to take into account if we refer to the topic of corrosion of a metal, which is why you should take and use prevention measures to reduce corrosion
There are organic and inorganic chemical compounds that when fixed in the body of the equipment that form a film between it and the corrosive medium, decreasing the speed of corrosion, these compounds are called inhibitors.
This method considers the use of small amounts of organic and inorganic compounds capable of forming a film or adherent barrier on the surface of the metal by electrical attraction or by a reaction, preventing access of the corrosive agents.
These compounds are characterized by high electrical charges at the ends of their molecules capable of being attracted by the surface to be protected; unfortunately this attraction is not permanent and a constant dosage in the middle is necessary.
This method is preferably used where there are fluid means of recirculation.
Source
Types of inhibitors:
The corrosion inhibitors can be classified according to several criteria, some of the most common are indicated below:
A) In response to its mechanism of action:
Anodic inhibitors
Cathode inhibitors
Mixed inhibitors
Adsorption inhibitors
The aforementioned inhibitors tend to increase the polarization both at the anode (anodic inhibitors), cathode (cathode inhibitors) and both at the same time (mixed inhibitors).
B) Considering its chemical composition:
*Organic inhibitors
Minio
Benzoates
Tannins
*Inorganic inhibitors
Chromates
Phosphates
Nitrites
Borates
Silicate
C) In response to its application
Inhibitors in vapor phase
Pickling inhibitors
Inhibitors for alkaline solutions
Inhibitors for chloride solutions
Inhibitors for drinking water
Inhibitors for boiler water
Inhibitors for petroleum products
Inhibitors for paints
Inhibitors for reinforced concrete
Inhibitors for fats and oils
Anti-freeze inhibitors
How to choose a good inhibitor?
When choosing a corrosion inhibitor, several things should be considered:
The materials that will be protected
The effective time of protection (1 week, 1 month, 1 year, etc.)
The method of application (immersion, sprinkling, brushing, etc.)
Type of protection required (in process, storage or shipment)
Handling the piece and removing the fingerprint
Type and thickness of the desired coating
The most common bacteria develop at potentials close to or below 0 and pH between 6 and 9.
For more information visit the following links
Comment * UpVote * Follow * Reestem
Thank you.
Really well written post there mate, well done :)
Thank you! I invite you to see the rest of my posts, I see that you like science
To the question in your title, my Magic 8-Ball says:
Hi! I'm a bot, and this answer was posted automatically. Check this post out for more information.
Great post.!! :)