TRANSISTORS: THE COMPONENT THAT CHANGED THE WORLD (AN OVERVIEW).
Just before now, before transistors came into existence, vacuum tubes has been the most important component of an electronic device. Its an electron tube or a valve used to control electric current. The vacuum tubes are bulky in nature and require higher operating voltage and power to function. It consumes a lot of power and has a lower efficiency. Due to inefficiency, short life spam and high-power consumption, there was need for another device that can work like the vacuum tube more efficiently, that consumes less power and yields a greater output. This paved way for the Transistors.
image credit
BJT TRANSISTOR
In the year 1947, three American physicists Walter Brattan, John Bardeen and William Shockley practically implemented a point-contact transistor at Bell Labs. This was a more powerful device that can overcome all the fundamental limitations of the vacuum tube.
Transistor is a semiconductor device that can conduct power and has insulating ability. It can act as a switch and as an amplifier, it converts audio waves to electric waves. They are smaller in size and has a much longer life span compared to vacuum tubes. It can equally operate under lower voltage.
A Transistor functions the same way a vacuum tube functions, but the difference is that it makes use of semiconductor. They are practically used in every modern electronic circuits; digital circuits, microprocessors, memory chips, Integrated circuits (ICs) you can name it, as long as electronics is concerned, transistors play a major role in its circuitry.
There are two basic types of transistor in common use today
Bi-polar junction transistor (BJT) and
Metal-oxide field-effect (MOSFET).

BJT TRANSISTOR
image credit

MOSFET TRANSISTOR
image credit
But in this lesson, we are focusing more on the Bi-polar-junction-transistor(BJT), which is the most commonly used and its also easy to understand and assimilate.
The BJT Transistor is the most common transistors to be produced in larger, it conducts suing majority and minority carriers, it’s a combination of two junction diodes and its formed as a p-type semiconductor or n-type semiconductor. This thus produces P-N junctions, a base emitter junction and a base collector junction. Transistors are built by stacking three different layers of semiconductor materials together, some of this semiconductor are doped (having extra electrons) and others have their electrons removed that’s how we came about the N-type (the ones that have extra electrons in them and the P-type (the ones that have their electrons removed).
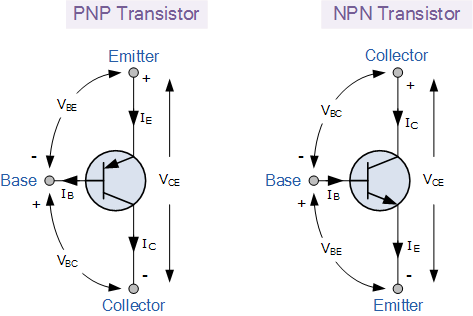
Bipolar Junction transistors has three terminals connected to a three-doped semiconductor and its of two types, the P-N-P and N-P-N (by stacking P over N over P or by stacking N on top of P on top of N).
The NPN transistor is designed in such a way as to pass electrons from the emitter to the collector. When the transistor is in ON, the current flow is in between the collector and the emitter of the transistor, the emitter then emits electron into the base. Based on the minority carriers in the P-type region, it allows for greater current flow and faster operation, thus making the NPN type of BJT the most commonly used transistors today.
The P-N-P transistor is made up of a layer of N-doped semiconductor material between the two layers of the P-doped semiconductor material. The base still controls the flow of current but its in the opposite direction (from emitter to collector). Instead of the emitter emitting electrons, it emits holes which means that no electron is present. The PNP and NPN transistors works in the same way but the major difference is that PNP transistors flows in opposite direction of the currents that flows in the NPN transistor.
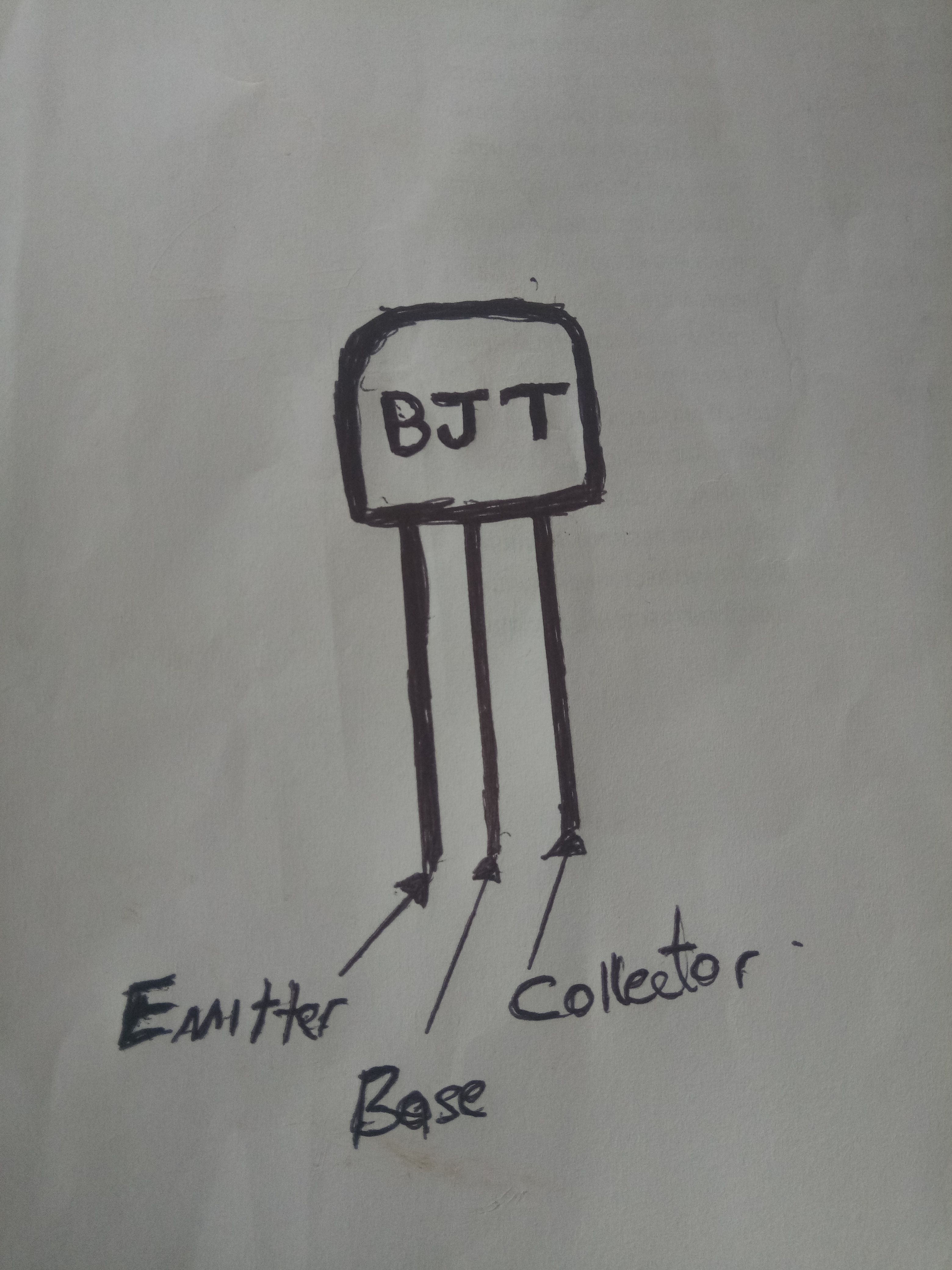
A transistor has three different legs or terminals,
Base - this is responsible for activating the transistor itself,
Collector– which is the positive lead and
Emitter – which is the negative lead.
How does a transistor work?
A transistor is kind of like an electronic valve, its like a relay or an electronic switch that can be used to turn current on and off or as a relay that can be used to regulate circuit or current.
A Transistor can either work as a switch or as an amplifier.
Working as an amplifier –
When a transistor works as an amplifier, it takes a smaller electric current at one end and makes it bigger, it amplifies the current to a bigger current at the other end, its kind of a current booster. Let’s take a speaker and microphone for instance, you speak through (sound input) the microphone and at the other end, it gets to the speaker which then amplifies it through and the sound becomes louder. William Shockley once explained the amplification mode of a transistor “if you take a bale of hay and tie it to the tail of a mule and then strike a match and set the bale on fire, if you compare the energy expended shortly thereafter by the mule with the energy expended by yourself in striking the match, I guess you will understand the concept of amplification.” Transistors are special because they can amplify electrical signals, they can turn a low power signal (input) to a higher power (output). That’s why they are used in radio devices, microphones, speakers etc. for amplification.
Three most common transistor amplifiers are:
Common emitter,
Common collector and
Common base.
Common emitter amplifier transistor –
This is one of the most common transistor arrangements in the market today, here, the emitter is tied to a voltage common to both the base and the collector or ground, the base then becomes the signal input while the collector becomes the signal output.
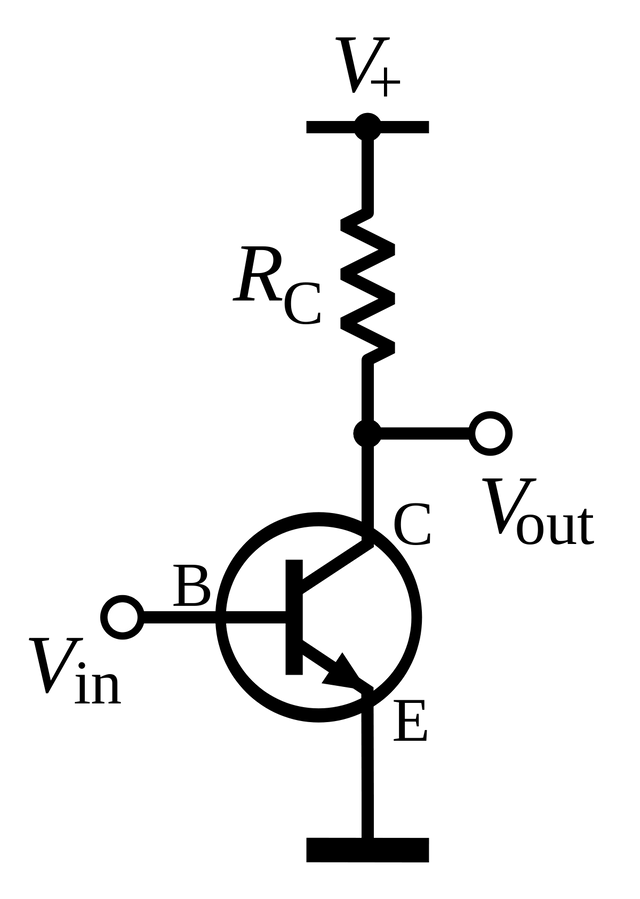
COMMON EMITTER
image credit
Common collector amplifier transistor–
When the collector pin is tied is tied to a common voltage, we have the base as an input and the emitter as an output. This is also known as emitter follower, it does not do voltage amplification, but it can be used as a great voltage buffer.
COMMON COLLECTOR
image credit
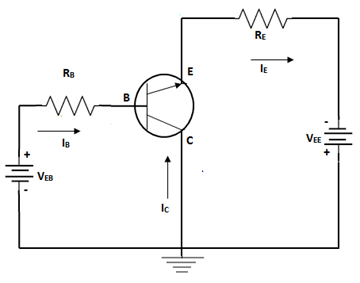
Common base amplifier transistor –
This is not in common use unlike the previous two, here the emitter serves as the input, the collector as the output and the base is always the same. Common base circuits works best when used as a circuit buffer, it can take an input current at a low input impedance and deliver same current to a higher impedance output.
COMMON BASE
timage credit
The above listed amplifier transistors all have areas in which they are mostly applied, be it in current amplification, voltage or buffering
Working as a switch –
Basically, a transistor works same way a relay works, it switches current flow on or off. This is applicable in most computer memory chips which is made up of millions of tiny transistors which can be individually switched on or off, since each transistor can be in two different states, with millions of Transistors put up together to make a chip, it can store millions of binaries and as many characters, letters and numbers as possible. Micro-controller chip for example, can hold a whole lot of zeros and ones.
Transistor switches are mostly used in building circuit blocks, they are used in making logic gates, both AND, OR, NOT, NAND, NOR, OR gates , which then can be used in creating micro-controllers, microprocessors and other integrated circuits which the computer systems use to process information and make decisions.
Advantages of a transistor
It has a longer life span compare to a vacuum tube.
They are readily made available, smaller in size, cheap and affordable,
They consume less power.
It has a low operating voltage.
Transistors are mostly used in all electronic circuits and devices.
Reference:
What does a transistor actually do?
So amazing ...
Although i dont flow with some of this things .. But i know they are amazing
Nicely highlighted ...