THE FUTURE IS HERE: 3D BIOPRINTING
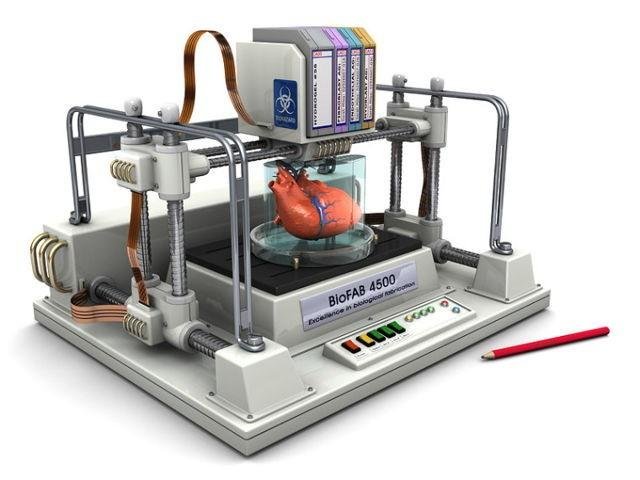 THE BIOPRINTER
[Credits](https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=3D+bioprinting&oq=3D+bioprinting&aqs=chrome..69i57j0l3j69i60.6595j0j4&client=ms-android-tecno&sourceid=chrome-mobile&ie=UTF-8#imgrc=MKDeQAVE2RAztM:)
THE BIOPRINTER
[Credits](https://www.google.com.ng/search?q=3D+bioprinting&oq=3D+bioprinting&aqs=chrome..69i57j0l3j69i60.6595j0j4&client=ms-android-tecno&sourceid=chrome-mobile&ie=UTF-8#imgrc=MKDeQAVE2RAztM:)Just like last week when I talked about the bionic eyes. Hmm, the bios are taking over the world of tech. The bionic eyes was made to replace blind eyes and now what do we see? THE 3D BIOPRINTER The printer that prints human tissues that prints human tissues that could replace real ones. Allow me to introduce to you in grand style THE 3D BIOPRINTER.
According to the Wake Forest University, North Carolina, researchers unveil that they just created a 3D bioprinter that could produce organs, tissues of the dummy and this time not dummies but they could practically replace indigenous ones. Dated Feb, 15 2016.
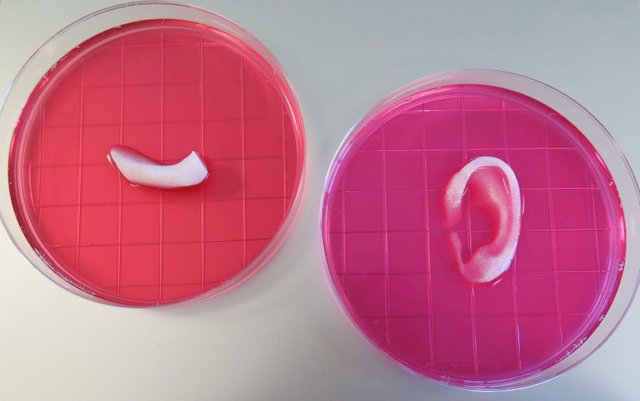

The above was the outcome of the bioprinting done at the University a year ago which showed they actually were successful with the bioprinting discovery. Little did they know that Todd Goldstein, a researcher at Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, was also researching about 3D bioprinting as at the time. Although, the first patent related to bioprinting was filed in 2003 but it was not granted until 2006 in the United States. Well, let's not talk about how it started, let's talk about the most important and notable things about it.
The Process of Bioprinting
According to Wikipedia, the normal procedure of bioprinting is done in three steps:
1 Pre-bioprinting
In this step One, everything needed for the main bioprinting process is put in place. This process involves making out the model of the tissue or organ you want to bioprint and also choosing the material to be used for the bioprinting. Please put in mind that the biopsy of the organ must be obtained.
2 Bioprinting
This is the main process and the major technologies employed are the computer Tomography also known as CT and the Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan.
In the second step, the liquid mixture of cells, matrix, and nutrients known as bioinks are placed in a printer cartridge and deposited using the patients' medical scans.[11] When a bioprinted pre-tissue is transferred to an incubator, this cell-based pre-tissue matures into a tissue.
The 3D bioprinting of body organs and tissues involve distribution of cells onto a biocompatible scaffold. This distribution is done to enable layer by layer approach to "generate tissue-like three-dimensional structures". Although bioprinting of crucial organs has been shown to lack some vital elements which you can check here for.
3 Post bioprinting
This step is as important as the bioprinting itself because this step is required to keep the bioprinted material or structure stable. Well, a 3D bioprinter might as well overlook this process and have his effort crumble before his eyes. In the process of maintaining stability of the bioprinted material, the chemical and mechanical stimulation are required. Now, let's go to the approaches...
The Bioprinting Approach
Without taking much time, bioprinting is slated into three appraches:
1 Biomimicry
Just as the name suggests it is the mimicry of natural organs but just in case there's need for further disintegration. Let's say, it's the act of copying a natural system, organ, tissue given by nature just for the sake of eliminating complicated human problems.
2 Autonomous Self Assembly
This approach relies on the physical process of embryonic organ development as a model to replicate the tissues of interes
Well, this might sound strange but it simply explains the process in which unarranged cells, tissues arrange themselves automatically to resemble evolving cells, tissues.
3 Mini tissue
This is the third approach and is a combination of the first two approaches that is biomimicry and autonomous self assembly. How does that work? It builds small functional components into bigger tissues and organs using two strategies.
The first strategy is when self-assembling cell spheres are arranged into large scaled tissues by using natural designs as a guide. The second strategy is when designing precise, high quality, reproductions of a tissue and allowing them to self-assemble into large scaled functional tissue
These 3 approaches are needed if a three dimensional biological structure must be printed.
Organovo regenerative Medicine Comapny were first to begin the commercialization of bioprinting.

GIF made by @foundation
Proud Member of @steemstem
Proud Member of @genesis-project
Thank you for your time!!
That little boy, @pearlumie.
Thats is helpful, people will no longer die in worries , this will go a long way helping those in want. If i may ask, does it has side effect, and can it be permanent with out going for re-fixing of the implanted part.
It can be permanent without re-fixing. There just might be some side effects if a vital organ was printed... I thought I mentioned it in the post
O yes you did ,thanks.
Thanks for dropping by
I am a strong believer that science is good but cannot replace God. Nice research
Correct!!
Wow!
Amazing discovery