Membrane is the part that covers or wraps the cell There are two types of membranes
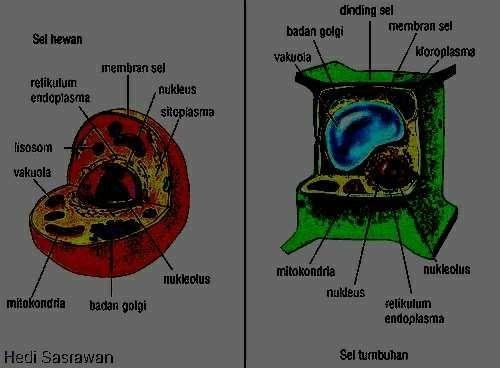
Cells are: the basic parts that make up every cell organ that functions as a living thing. The cell structure consists of parts of membranes, organelles, and cytoplasm. The structure of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is different. Similarly, the cell membrane structure of plant cells and animal cells using the methods described above. The structure works and functions to perform cell functions such as metabolism, gene storage, cell division, and DNA synthesis. With it the cell can work with a maximum of parts of plants and animal cells.
1. Membrane
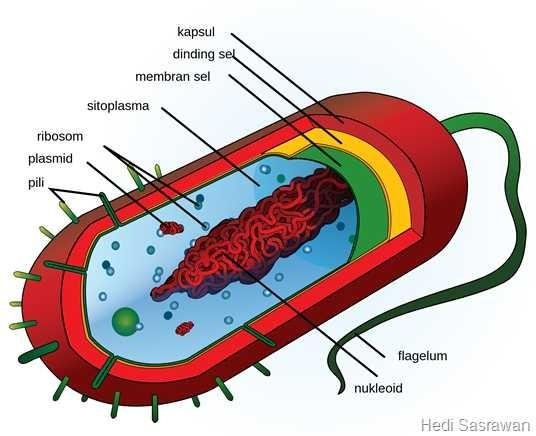
Membranes are: parts that cover or wrap cells in plants and animal cells. There are two types of membranes (outer covering and cell coating) ie cell membranes and cell walls. Its function is equally to protect the living cells of plants and animals, wrap the cells, and regulate the inflow of substances very normally on substances and cell membranes also serve as a medium of communication between cells and the environment. Cell membranes are selectively permeable and are able to regulate what enters and exits the cell, thus facilitating the transport of the materials necessary for survival. Movement of substances in the cell membrane can become passive and become active when there is energy. Membranes also retain potential cells. Cell membranes work like filters that prevent the virus from entering the cell.
2. Cell Wall
The cell wall is: a rigid and strong layer beyond the alleged that makes the cell membrane that surrounds several stages of cell type. Cell walls are characteristic of plant cells, some types of bacteria, and algae. The function of cell walls is to provide strength and structural support to stress mechanical and infections. The liquid in the plant cell can expand so as to cause turgor pressure. This pressure if nothing is restrained, can cause the cell to rupture. So from that, it takes a cell wall in plant cells.
3. Organel
Organelles are: the components that make up the cell as well as the organs in the body of mammals. This organelle is essential for maintaining blood and cell stability and is useful for supporting all cell activities and functions in the fluid to thrive in plant cells.
4. Cytoskeleton
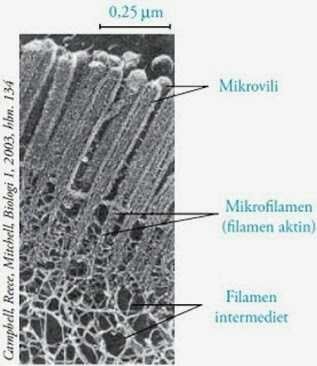
The cytoskeleton is: the cell skeleton. Its function is to support the structure of cells and other organelles in the cell. The cytoskeleton also forms centrioles. The cytoskeleton consists of microfilaments, middle filaments, and microtubules. Cytoskeleton is owned by all types of cells. The eukaryotic cells contain three types of cytoskeleton filaments, namely microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. The three filaments are connected to each other and mutually coordinate. The cytoskeleton provides structure and shape to the cell, and by macromolecules of some cytosols that increase the level of macromolecule collecting in the compartment. Cytoskeletal elements interact closely with cellular membranes. A small number of cytoskeletal drug molecules have interacted with microtubule activity. This compound has proven useful in studying cytoskeleton and applying it clinically.
5. Ribosome
Ribosomes are: small organelles, solid parts of plant stems and on the feet of animals, and are not membembran but play an important role as a place of synthesis and protein. In a cell there are many ribosomes scattered in the cytoplasm and attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are owned by all cell types. Works quickly and is very good for the cells The free ribosome can move anywhere in the cytosol except in the nucleus of the cell and other organelles. Proteins formed in free ribosomes will be excreted from the cytosol and used by cells.
6. Retikulum Endoplasma
The endoplasmic reticulum or abbreviated RE is: organelles in the form of cells in the bag such as the membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum exists only in eukaryotic cells. There are two types of RE that are rough RE and RE fine. Rough RE there are many ribosomes and it is very important to keep the stability of the cell and stick with the cell nucleus. While the RE fine has no ribosome. The crude RE function is for protein synthesis. The subtle RE function is for lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs that are essential for maintaining cells in Robson for cells attached to the animal portion.
Protein and fats with the amount of 30% to 50%.
The rest are certain enzymes that are needed when protein synthesis, fat metabolism, and detoxification.
The word Reticulum comes from the word reticular which means woven yarn or nets. Because it is centered on the inside of the cytoplasm (endoplasm) and because its structure is partly woven and to a large extent present in the endoplasm. With the discovery of this Endolplasma Reticulum a cell can no longer be thought of as a bag containing enzymes, RNA, DNA, and solutions of materials bounded by an outer membrane such as in primitive bacteria
7. Golgi Agency
Golgi or Golgi apparatus are: membrane-bound organelles that act as cells in the cell excretion system. The form of flat pockets piled-pile starting from large or small. Golgi bodies can be found in almost all eukaryotic cells. Cells that surround all the sacs from the attachment of cells to the animal part.
The structure of a golgi body resembles a bundle of disc-shaped bundles and becomes a series of narrowed vessels at the ends. The visible vessels serve to collect and wrap carbohydrates and other substances to be transported to the cell surface. Simultaneously contributes material for the formation of cell walls, especially in plant cells.
8. Mitochondria
Mitochondria are cell organelles that function as a respiration cell for living things. Broadly speaking, the respiration stages in plants and animals pass through the same path, known as the cycle or cycle of the Krebs. Mitochondria are often referred to as "energy generators" for cells because they produce the most ATP energy for cells. Mitochondria contain a number of enzymes and proteins that help the carbohydrate and fat process obtained from the foods we eat to release energy. Mitochondria have two membrane layers, namely the outer membrane layer and the inner membrane layer.
9. Lysosome
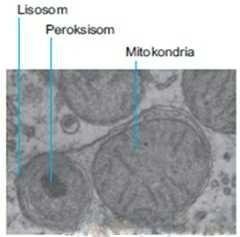
The lysosome is: the cell organelle in the tangible part into a rather rounded pouch surrounded by a single membrane. It contains hydrolytic enzymes to control intracellular digestion. The function of lysosomes is: the form of the cell membra on the live cell part to process in the pockets in the weak yamg and open up the gentle bunch of cells to digest macromolecules such as polysaccharides, lipids, phospholipids, nucleic acids, and proteins. Lysosomes can be found in almost all animal cells except red blood cells.
10. Sentriol
Sentriol is: organelles that play a role in important membrane cells in the body of animal cell division through the process or with digestion called mitosis. Sentriol is found only in animal cells. Although plant cells do not have centrioles, plants can still divide the cells through the cleavage path of open pores to enter cells.
11. Plastids
Plastids are: organelles that produce a dense color of trawl on plant cells when opening the temperature and removing the substance in the cell. Plastids are present only in plant cells. Plastide function is very important because it produces chemical substances in plants and this is where photosynthesis takes place and produce energy ATP for plants. Plastids are made up of three types: chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leukoplasts. These are further details and complete.
12. Peroxisomes
Peroxisomes are: organelles contain very trash proteins in living cells and gently on receptors enclosed by a single membrane called metronidazole and made of lipids. Peroxisomes can be found in almost every live eukaryotic cell. The function of peroxisomes is to simplify cells to multiply and to chain long fatty acids through the process of oxidation beta. In addition, peroxisomes also function to transfer the hydrogen to oxygen and neutralize the toxins produced by the transfer process when it fails all the cells destroyed and the plants to wither.
13. Vakuola
Vacuoles are: organelles in the form of cavities covered by membranes (tonoplasts) containing liquids such as water, organic acids, enzymes, amino acids, lipids, glucose, alkaloids, mineral salts, acids, and bases. Vakuoles can be found in almost all cell types. It's just that the size of vacuoles in plant cells is very large even dominate the volume of plant cells. Vakuola in small animal cells but more than one. Vakuola function is as a storage place.