Psychiatry #1 - Psychiatric Emergencies! Neuroleptic vs Serotonin Syndromes

Hey guys, sorry for the delay again. I’ve been busy with studies (+- socializing, hahaha). Anyway, today I’ve decided to cover the four medical emergencies or emergency situations in the Psychiatry. Most of these conditions are related to the administration of anti-psychotic, especially among schizophrenic patients as they require anti-psychotics to alleviate their symptoms. The 2 syndromes that are discussed in this blog are the Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome and Serotonin Syndrome.
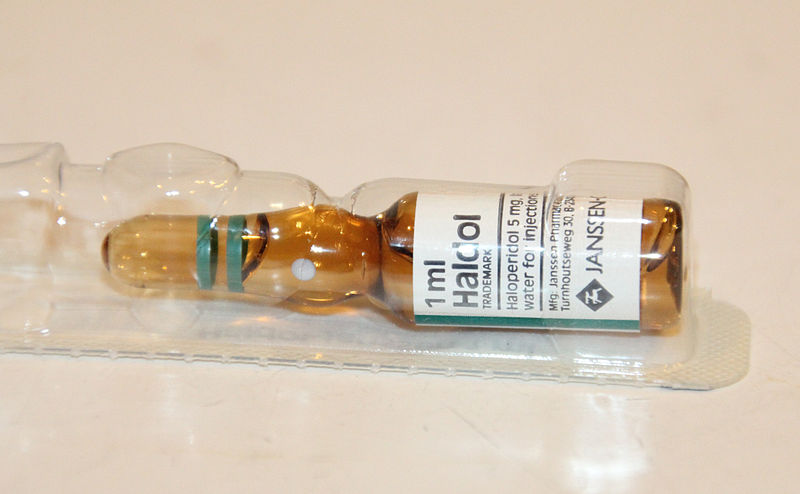
The main reason why I did this article today is because I saw a patient in the ward that has generalized rigidity, as in the patient is generally stiff. She was on anti-psychotics – Tablet Risperidone and Tablet Olanzapine for years. She came to the main hospital in Kuala Lumpur with the complains of fever, high blood pressure and generalized body stiffness. The emergency department managed to withdraw her blood to look for Creatine Kinase (CK) level, and it was sky high. They have decided to admit her to the ward for further management.

Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) is thought to be a rare, potentially fatal, reactions that happen due to anti-psychotic medications. The most common drugs blamed for this condition are the Haloperidol and Fluphenazine. Mortality of this disease has declined tremendously recently as there are more awareness of the disease, earlier diagnosis and better intervention. Up to 3% of people taking the first generation anti-psychotics can develop this syndrome.
Associated Medications:
- Antipsychotics – Chlorpromazine, Fluphenthixol, Haloperidol, Fluphenazine, Olanzapine, Risperidone, Clozapine, Quetiapine
- Antiparkinsons – Levodopa, Anti-cholinergics, Amantadine
- Anti-Depressant – Venlafaxine, Clomipramine, Trimipramine
- Anti-Emetics (to suppress vomiting) – Metoclopramide, Promethazine
- Others – Lithium, Oral Contraceptives, Carbamazepine
I’m sure many of the Steemians covered Schizophrenia before because it is such a mystifying condition that sparks interest in many people. If you guys have read about Schizophrenia, I’m pretty sure you guys have some idea about the Dopamine receptors theory which is related to Schizophrenia. People that experience Schizophrenia probably has many dopaminergic activities going on in their brain compared to individuals without it. Hence, the mechanism of action of the anti-psychotics is the blockade of the Dopamine receptors to eliminate psychotic symptoms such as hallucination, delusions and negative symptoms.
The current theory of NMS involves the excessive blockade of Dopamine receptors in the brain. Central dopamine receptor blockage at the hypothalamus region may cause hyperthermia (fever > 38 degrees Celcius) and other signs of dysautonomia such as labile blood pressure, tachypnea (shortness of breath), and diaphoresis (excessive sweating).
Interference to the nigrostriatal pathways in the basal ganglia may lead to Parkinson-like symptoms such as rigidity and tremor. Take note that in Parkinson, the individual lacks of dopaminergic activities in the brain. That’s why Dopamine is given to Parkinson patients to alleviate symptoms such as tremor, rigidity and bradykinesia.
Some even theorized that antipsychotic drugs facilitates the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum within the muscles. This might explain how individuals with NMS can experience rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of muscles), muscle rigidity and hyperthermia.
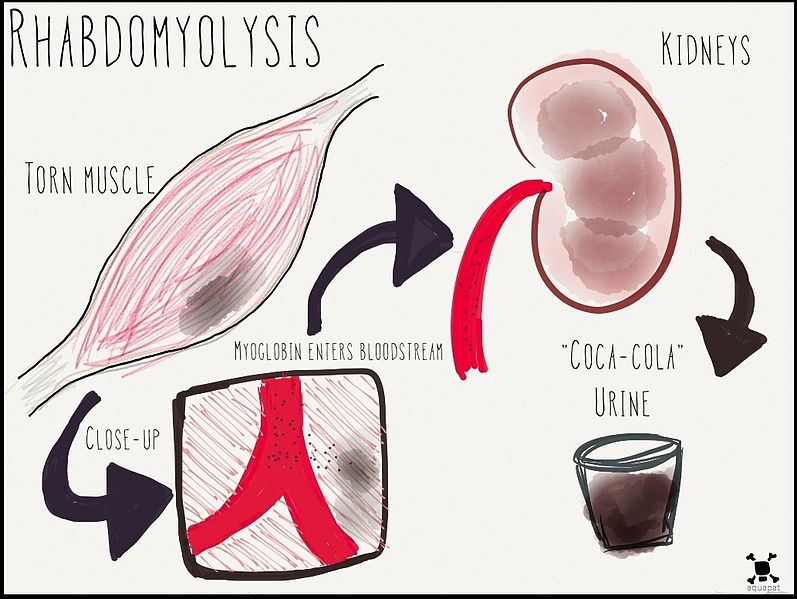
Hence, the clinical features of Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome are:
- Motor – Generalized muscle stiffness, which may affect the muscles of respiration and swallowing causing shortness of breath and difficulty in swallowing, respectively
- Mental - Reduced level of consciousness
- Autonomic – Unstable Blood Pressure, fast heartbeat, excessive sweating, salivation, urinary incontinence
- High fever (>38 degrees Celcius)
So if a patient presented to the emergency section of the hospital with the following symptoms and also knowing that the patient has schizophrenia, what sort of lab investigations can be done to aid in the diagnosis?
- Full Blood Count – May show increase in White Cell Count maybe due to the breakdown of muscles
- Liver Function Test – Elevations of liver enzymes are common
- Renal Profile – Electrolyte Imbalances are common too as well as breakdown of muscles can cause acute kidney injury, which results in high creatinine and urea levels
- Arterial Blood Gases – May show Metabolic Acidosis
- Urine Screening for Myoglobin as breakdown of muscles can cause presence of myoglobin in the urine
- Serum Creatine Kinase – It is an important lab investigation as severe rigidity leads to higher Creatine Kinase level in the blood. The Creatine Kinase level can shoot up to 100, 000 international units/L.
So how individuals with NMS are managed?
First and foremost, we should stop the offending agent. In this case, the antipsychotics. Supportive managements are important such as giving oxygen, correct the labile blood pressure with fluids and reduce the temperature by giving anti-pyretics, cooling blankets, ice packs, and cooled IV fluids. Benzodiazepines such as Clonazepam can be given to resolve the behavioral disturbances. Dantrolene can be given as it is a direct-acting skeletal muscle relaxant. Once all the symptoms are gone, it is recommended to wait for at least 2 weeks before re-commencing the antipsychotic medications.
Serotonin Syndrome
Unlike the Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome which is often associated with chronic use of Anti-psychotic especially the first generation ones, Serotonin Syndrome is often linked with drugs which escalates the level of serotonin in the synapse (also known as serotonergic drugs) such as the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs), Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs), Mono Amine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs), and Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCA). These drugs are often use to treat depression, thus Serotonin Syndrome is more likely to occur in individuals with depression. Other medications which are often associated with the increase level of Serotonin in the synapses are:
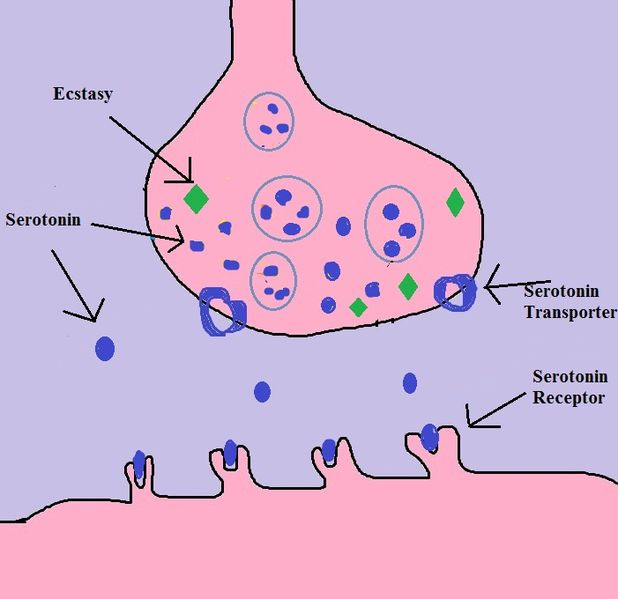
- Triptans (which treats headache and migraines) – Sumatriptan, Zolmitriptan, Frovatriptan
- Drugs of Abuse – Amphetamines, Cocaine, Ecstasy, LSD
- Dopamine agonists (treats Parkinsonism) – Amantadine, Bromocriptine, Levodopa
- Miscellaneous – Buspirone, Lithium
Many cases of Serotonin Syndrome involves the ingestion drug combinations, especially those I’ve mentioned above. In the central nervous system, serotonin receptors are involved in attention, behaviours, and thermoregulation. In the peripherals, it is also found in the blood vessels, uterine, bronchus and even in platelets. Serotonin Receptors and also known as the 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors have many complex functions in the body but they are often to be the main culprit in causing Depression as lacking of serotonin neurotransmitter causes the depression symptoms such as low mood, lack of concentration, and having suicidal ideation.
Based on Sternbach’s Diagnostic Criteria for Serotonin Syndrome, it must include at least 3 signs and symptoms of the following:
- Agitation/restlessness
- Sweating
- Diarrhea
- Fever
- Hyperreflexia
- Ataxia
- Changes in mental state
- Myoclonus
- Shivering
- Tremor
Furthermore, Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome must be excluded and thus the criteria of “no concurrent ant-psychotic dose changes prior to abuse” is included. The other criteria is that physicians must also exclude infection, metabolic disturbances, substance abuse and withdrawals.
The symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome are often placed in the clinical triad of:
1 – Cognitive effects: headache, agitation, confusions, coma
2 – Autonomic effects: shivering, sweating, hyperthermia, fast heartbeat, nausea, diarrhea
3 – Somatic effects: Myoclonus (or muscle twitching), Hyperreflexia, tremor
In comparison with Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome, this syndrome has shorter onset of action as it can happen less than 12 hours after ingesting different types of serotonergic drugs. In the physical examination, Serotonin Syndrome tends to show hyperreflexia while in Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome, reflexes are commonly reduced. Pupils are dilated in Serotonin Syndrome and not in NMS. Bowel sounds are more active in Serotonin Syndrome as the involvement of serotonin receptors in the bowel. Identical features of both syndromes are the labile blood pressure, hyperthermia, fast heartbeat, shortness of breath, hypersalivation, excessive sweating, altered mental consciousness, and rigid muscle tone.
Lab investigations to aid the diagnosis?
It is well known that Serotonin Syndrome is a clinical diagnosis and do not really require laboratory involvement to confirm the diagnosis. However, certain tests are helpful to diagnose the condition:
- Full Blood Count – Elevated White Cell Count
- Creatine Kinase – Elevated CK level
- Drug toxicology screening – to determine whether the individual has abused cocaine, LSD, or PCP before
How do we treat this condition?
In severe cases, admission to the Intensive care unit is important. For overdosed patients, giving charcoal or gastric lavage might be helpful to remove the remaining drugs in the gastro-intestinal system. IV access should be established to correct fluid volume and reduces the risk of muscle breakdown. Benzodiazepine can be given to alleviate mental changes, and anti-pyretic to treat fever. The majority of the cases will resolve within 24-36 hours after adequate supportive treatment.
In short, psychiatric emergencies can be quite debilitating as the symptoms are indeed scary. Imagine if you have found someone that is still conscious and yet having a very stiff body (corpse-like), you might freak out. Knowing the condition definitely aids in the treatment part as the main stay of management is to avoid the offending agent and provide supportive care to the symptoms. Moreover, taking good history from the patient is essential as the cause of the problem is different (chronic antipsychotic use vs ingestion of multiple serotonergic drugs) and yet they might present very similarly. Last but not least, education to the patient is essential to avoid future "attacks" of similar symptoms. With that thanks for reading :)
References
- Hyland D. Four Medical Emergencies in Psychiatry. www.askdoctorclarke.com. PDF File.
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome. UptoDate. Retrieved on May 18, 2018, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/neuroleptic-malignant-syndrome
- Serotonin Syndrome. UptoDate. Retrieved on May 19, 2018, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/serotonin-syndrome-serotonin-toxicity?topicRef=4829&source=see_link
- Sternbach H (1991) The Serotonin Syndrome. American Journal of Psychiatry 148, 705-13. PDF File
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome or Serotonin Syndrome?. Medsafe. Retrieved on May 19, 2018, from http://www.medsafe.govt.nz/profs/PUArticles/Dec2012Neuroleptic.htm
- Triptans. Wikipedia. Retrieved on May 19, 2018, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triptan
- Serotonin Syndrome. Wikipedia. Retrieved on May 19, 2018 from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotonin_syndrome


Would you consider tetanus in a patient with generalised rigidity in this setting? Or are vaccination rates generally quite good over there?
oh yes tetanus. From what I know, tetanus is caused by the organism Clostridium tetani. This bug causes muscle rigidity. Based on what's written on the books, serotonin syndrome and neuroleptic malignant syndrome's rigidness are caused by the increase of calcium release at the muscles. Tetanus vaccine would probably stop the tetanus toxins released by the Clostridium and not stop the calcium release caused by anti-psychotics or SSRIs. Thanks for mentioning though, quite a good question. I've never thought of this before.
You've been upvoted by TeamMalaysia Community :-
To support the growth of TeamMalaysia Follow our upvotes by using steemauto.com and follow trail of @myach
Vote TeamMalaysia witness bitrocker2020 using this link vote for witness