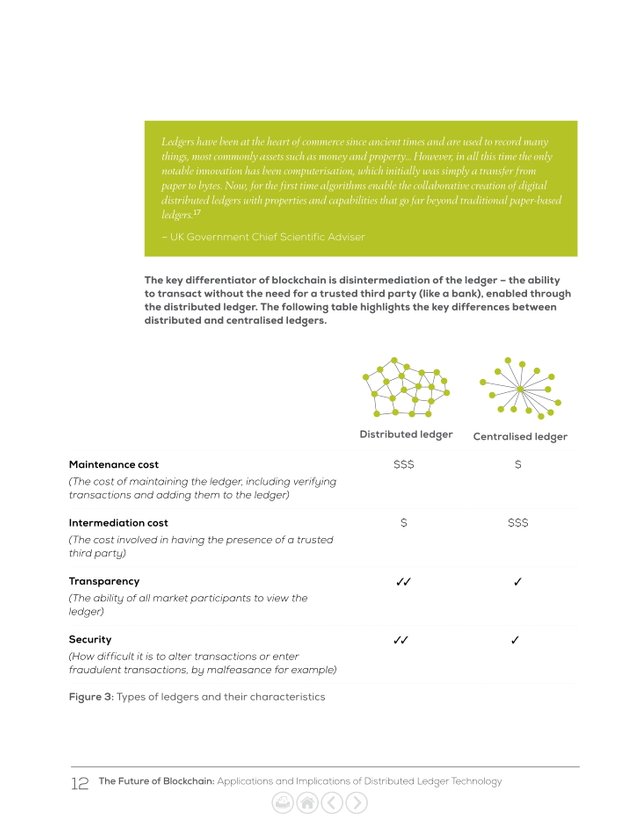
What makes distributed ledger technology different?
Historically, ledgers have taken two key forms: two-party (or “nostro-vostro”), and centralised. Two-party ledgers are based in traditional double-entry bookkeeping: when processing a transaction, one organisation will record a credit and the other a debit. In a centralised ledger, a central authority maintains and appends records to a single ledger, and may choose to show a copy of that ledger to other market participants.