Blockchain Made Easy: Part 2

Have you been having issues trying to wrap your mind around what the whole cryptocurrency and blockchain gist is all about? Relax and stay with us through a series of simplified articles to help you out with the dilemma. We started last week by discussing the history of money starting from commodity money to the advent of virtual currency. This week, we’ll be taking it from where we stopped.
What is Blockchain?
In simple words, Blockchain can be defined as a chain of the block that contains information. The technique is intended to timestamp digital documents so that it’s not possible to backdate them or temper them.
Blockchains could not be run without the Internet. It is comprised of several pieces: a database, software application, some connected computers, etc.
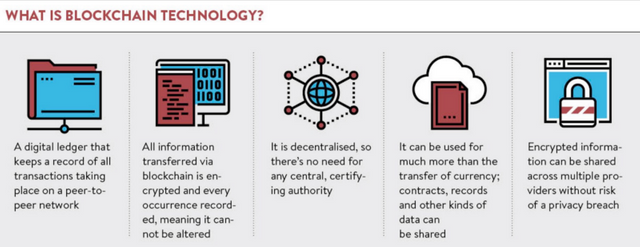
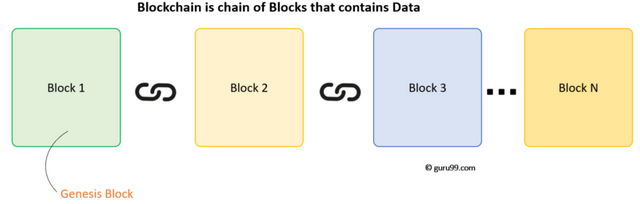
How Blockchain Transaction Works?
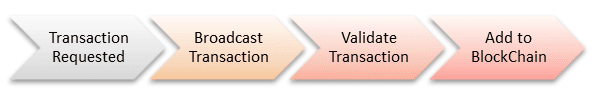
Step 1) Some person requests a transaction. The transaction could involve cryptocurrency, contracts, records or other information.
Step 2) The requested transaction is broadcasted to a P2P network with the help of nodes.
Step 3) The network of nodes validates the transaction and the user’s status with the help of known algorithms.
Step 4) Once the transaction is complete the new block is then added to the existing blockchain in such a way that is permanent and unalterable.
Why do we need Blockchain?
Here are some reasons why Blockchain technology has become so popular.
Resilience: Blockchains are often replicated architecture. The chain is still operated by most nodes in the event of a massive attack against the system.
Time reduction: In the financial industry, blockchain can play a vital role by allowing the quicker settlement of trades as it does not need a lengthy process of verification, settlement, and clearance because a single version of agreed-upon data of the share ledger is available between all stakeholders.
Reliability: Blockchain certifies and verifies the identities of the interested parties. This removes double records, reducing rates and accelerates transactions.
Unchangeable transactions: By registering transactions in chronological order, Blockchain certifies the inalterability of all operations which means when any new block has been added to the chain of ledgers, it cannot be removed or modified.
Fraud prevention: The concepts of shared information and consensus prevent possible losses due to fraud or embezzlement. In logistics-based industries, blockchain as a monitoring mechanism acts to reduce costs.
Security: Attacking a traditional database is the bringing down of a specific target. With the help of Distributed Ledger Technology, each party holds a copy of the original chain, so the system remains operative, even if a large number of other nodes fail.
Transparency: Changes to public blockchains are publicly viewable to everyone. This offers greater transparency, and all transactions are immutable.
Collaboration – Allows parties to transact directly with each other without the need for mediating third parties.
Decentralized: There are standards rules on how every node exchanges the blockchain information. This method ensures that all transactions are validated, and all valid transactions are added one by one.
Next week, we will be examining the available versions of the blockchain and their variants. Stay tuned!
Hi! I am a robot. I just upvoted you! I found similar content that readers might be interested in:
https://www.guru99.com/blockchain-tutorial.html
Congratulations @telos4africa! You have completed the following achievement on the Steem blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your Steem Board and compare to others on the Steem Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPDo not miss the last post from @steemitboard:
Vote for @Steemitboard as a witness to get one more award and increased upvotes!