The India's caste system in 4 points - A journey in India.

Yesterday, I was talking with my aunt about India and how little we know about its government and its society. I did some reasearch and I thought it could be interesting to share this story with you ;)
You have probably heard of the caste' system or the untouchable people in India, without being able to tell exactly what’s it all about.
Until yesterday, me neither, here is what I found.
Although it was abolished in 1947 by the constitution, the ancient Indian caste (“Jati”) system shapes the current Indian society.
1. What is it ?

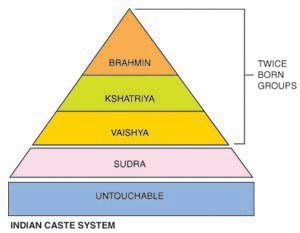
The ancient Hindu text “Manusmriti” tells us that the supreme being created Mankind in his body.
- From his mouth came the “Brahmas” a superior class populated by priests
- From his arm came the “Kshatriyas”, the warrior class
- From his his thigh came the “vaishyas”, the tradespeople, farmers’ class
- From his foot came the “sudra”, the servants’ class
Untouchables (“Dalit”) are excluded from the caste system. The system claims they have an unclean soul and no social status. They represent 18.43% of the 1.3 billion indian population.
2. How the belonging to a caste is done ?

Indian people don’t choose their belonging to a caste, it’s hereditary. They can’t change caste and they need to do their duties attributed by their caste.
The current Indian system has evolved and people can change jobs“but traditionally, Indian perpetuates with fatalism the ancestral craft.”
Indians are still doing endogamy and ideally want to marry a same caste person.
3. How to change caste ?
- Make money : Since 1991 low caste can start a business. Kalpana Saroj a Dalit woman married a 12 is now a successful entrepreneur who worth $112 millions !
- Positive discrimination : Since the abolition of castes in 1947 ,The Indian government tries to implement a positive discrimination policy. A Dalit elite emerged from it, but because of some resistance from the upper class, this policy isn’t efficient.
- Vote : Shashi Tharoor, a political writer said that Indian people vote for their own castes. The castes politics became a business. The vote isn’t a way to break caste but rather to compete it.
4. What about now ?

The social mobility allowed people to practice a profession without relations with their castes. Although deeply rooted in the Indian culture, the caste system is evolving and today, a middle class is exploding in Indian. The appartenance to this class bypass the caste system.
Today Ram Nath Kovinda an Untouchable is about to become president, Indian society is changing !